Figure 3.
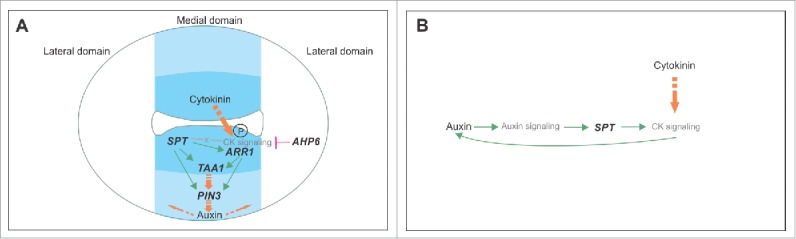
Models of the regulatory network in early gynoecium development integrating SPT, cytokinin signaling, and auxin signaling, and their synergistic interaction. (A) Previously published model of the regulatory network active in the ovary region in the young gynoecium.14 The transcription factor SPT enables cytokinin signaling at the medial region in part by transcriptionally activating the type-B ARR1 transcription factor. The protein becomes active upon phosphorylation by a phosphorelay cascade initiated when cytokinin is present. Subsequently, both SPT and ARR1 transcriptionally activate the auxin biosynthesis gene TAA1 and the auxin transporter PIN3, probably resulting in an auxin flux. SPT most likely also affects other components of the cytokinin signaling pathway. In the lateral domain, the cytokinin signaling repressor AHP6 restricts cytokinin signaling to the medial domain. (B) Model of the synergistic relationship between auxin and cytokinin signaling in the ovary region of the gynoecium. Auxin positively affects cytokinin signaling in a SPT-dependent manner, and cytokinin positively affects auxin production, thereby positively affecting auxin signaling.
