Figure 14. Use of a genetic approach to test a mitochondrial mechanism of toxicity of AgNPs.
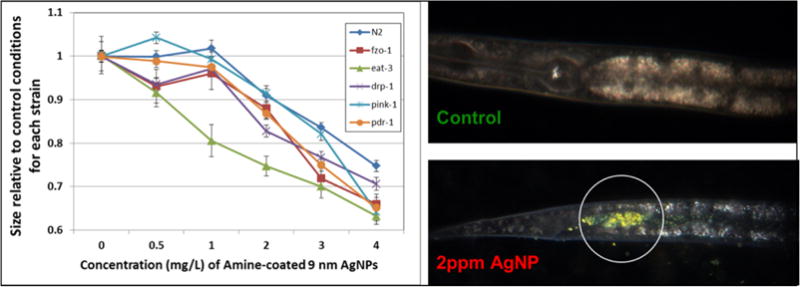
We tested the sensitivity of N2 and multiple mutant strains with deficiencies in mitochondrial homeostasis genes (drp-1, eat-3, fzo-1, pdr-1, pink-1) to exposure to 9nm (average diameter), amine-coated, positively-charged AgNPs. The graph depicts the relative length of control and treated animals after 72 h of growth from the L1 stage (synchronized), in MHRW, with UVC-killed UVRA bacteria. Error bars represent one standard error of the mean; experiment repeated twice in time, total n = 39–40 nematodes per dose per strain. Because aggregation of AgNPs was observed, we used hyperspectral imaging to verify ingestion after 48 h with a 2 ppm exposure. Ingestion was observed for all strains (N2 shown). Unpublished data from Victoria Harms, Laura Maurer, and Joel Meyer; AgNPs synthesized by Stella Marinakos; Cytoviva images taken and analyzed by Nick Geitner.
