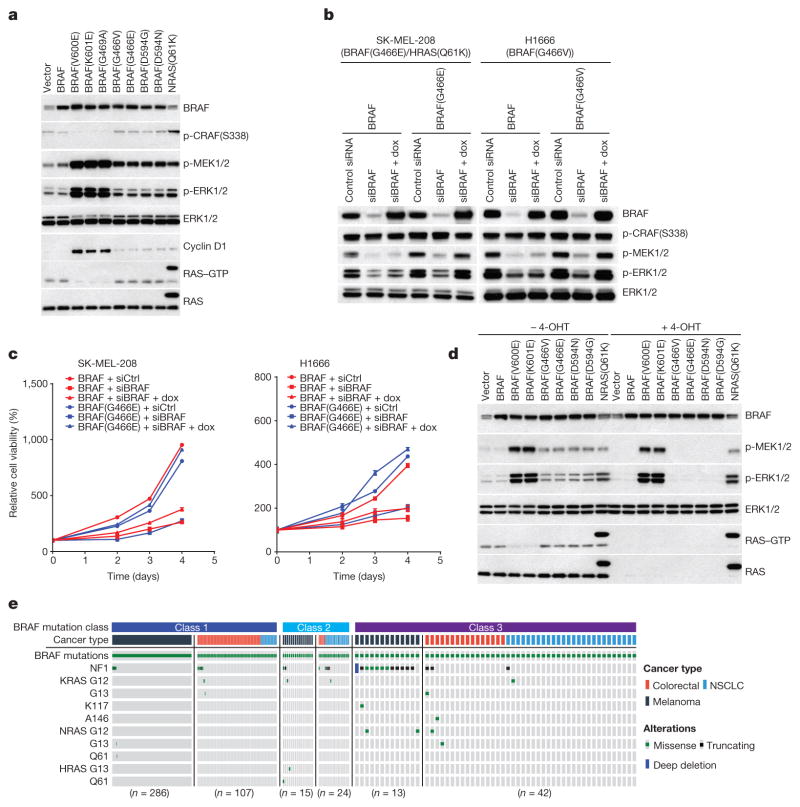
Figure 1. Activation of MEK/ERK by low-activity or kinase-dead BRAF mutants is RAS-dependent.
a, ERK signalling was assessed in NIH3T3 cells expressing the indicated BRAF proteins (30 ng ml−1 doxycycline, 24 h). b, c, Inducible wild-type BRAF or mutant BRAF (G466E or G466V) was introduced into H1666 or SK-MEL-208 cells. The indicated cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against the human BRAF gene. b, After 1 day, 106 cells of each cell line were treated with doxycycline (dox; 30 ng ml−1, for 24 h) and ERK was assessed. c, 3,000 cells of each siRNA transfected cell line were then plated in 96-well plates in medium with doxycycline. Cell growth was determined by ATP-Glo assay. Growth curves were generated with Prism 6 (mean ± s.d., n = 8). d, Expression of indicated BRAF proteins was induced (10 ng ml−1 doxycycline, 24 h) in the conditional RAS-less cells that were pre-treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) to knock out the last RAS allele. In a, b and d, Erk signalling was examined by western blot and RAS–GTP levels were determined by the active RAS pull-down assay. The gel source data are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1. e, Oncoprint showing co-mutation of class 3 BRAF mutants with RAS/NF1 in samples from cancer patients. The data were collected from http://cbioportal.org.