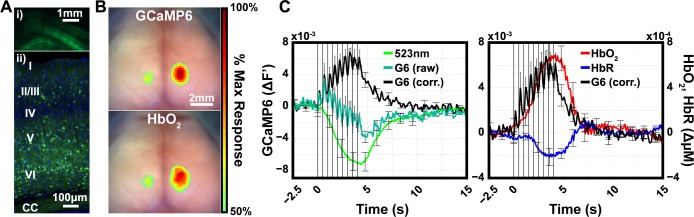
Fig 2. Thy1/GCaMP6 mouse model validation.
Based on previous studies, Thy1/GCaMP6 fluorescence should provide a signal predominantly driven by cortical neuronal neurons and that is faster than hemodynamic measures. (A) Epifluorescence (i) and confocal (ii) images of 50um coronal slices collected from a representative Thy1/GCaMP6 mice. GCaMP6 expression (green) is located throughout the cortex (i) and localized to neuronal soma (ii, blue-DAPI stain) and can be seen throughout cortical layers I-VI. (B) Map of stimulus evoked responses to electrical stimulation of left hindpaw (thresholded at >50% peak response) in the anesthetized state. (C) Time series of evoked responses sampled using masks created from the right half of the 50% peak response images in part B. Green reflectance (green trace, top panel) is used to correct raw GCaMP6 emission (teal trace) for changes in absorption due to hemodynamics using a ratiometric approach (see Methods; the corrected trace is black). The corrected GCaMP6 trace (black) is sensitive to each stimulus presentation (black trace, lower panel), whereas HbO2 (red) and HbR (blue) follow the slower, canonical hemodynamic response. Error bars are standard error of the mean. Data from 36 blocks across 7 mice are included in all evoked analysis.