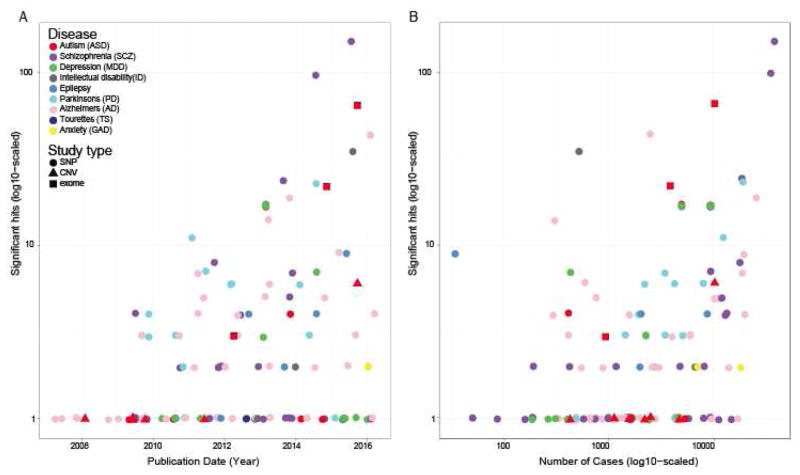
Figure 1. Burgeoning sample numbers have driven identification for loci contributing to several diseases.
A) Number of loci or genes implicated as a function of year. Across multiple neuropsychiatric diseases, common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) studies show substantial discovery, particularly for SCZ, but with notable recent gains in AD, PD. Several other adult diseases are beginning to detect some loci. Success in ASD has primarily been in identification of rare de novo variants causing disease (via copy number variation (CNV) analysis and exome sequencing). B) Number of loci discovered is largely a function of accumulating samples sizes. Common SNP data curated from https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/ on 1/25/17, using each disease name as a search term. ASD rare variants manually curated.