Fig. 1.
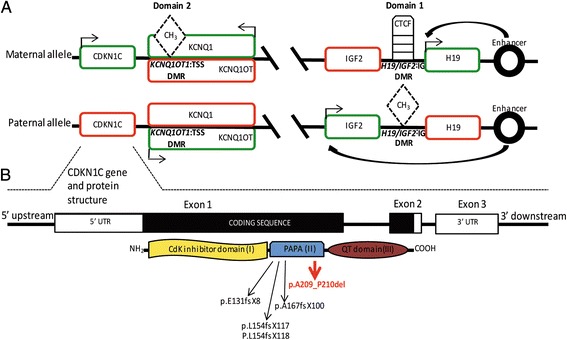
Epigenetic and genetic regulation of the 11p15.5 imprinted locus. As shown in (a), the 11p15.5 imprinted locus presents with 2 domains (Domain 1 and Domain 2) differentially regulated by H19/IGF2-IG and KCNQ1OT1:TSS DMRs, respectively. Transcribed genes are depicted in green, silenced genes in red. On the maternal allele, the effect of the enhancer promotes the expression of H19, the most proximal gene, but not of IGF2. This is the consequence of the CTCF binding to H19/IGF2-IG DMR located between the two genes. On the paternal allele, methylation of this DMR prevents the binding of CTCF, allowing the expression of IGF2 and the silencing of H19. At KCNQ1OT1:TSS DMR the opposite methylation pattern is observed. This DMR is methylated on the maternal allele and not on the paternal one. Thus, maternal repression of KCNQ10T allows the expression of CDKN1C and KCNQ1, while the expression of the KCNQ10T on the paternal allele inhibits the transcription of the flanking genes CDKN1C and KCNQ1. CDKN1C gene and protein structure are depicted in (b). White striped boxes identify the 5′- and 3′-UTRs and the black portion represents the coding sequence of the gene. CDKN1C encodes for P57 protein (alias KIP2), composed of the three functional domains depicted with different colors. Black arrows indicate previously identified truncating mutations inside the PAPA domain; red arrow points out the susceptibility variant p.A209_P210del identified in this paper
