Fig. 1.
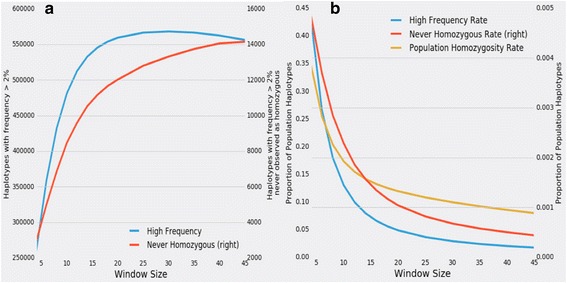
Effect of window size on haplotypic diversity and lethal haplotype detection. a As the size of the window expands, many more distinct haplotypes are detected genome-wide. However, fewer of the newly detected haplotypes are common as window size increases, and the number of common haplotypes that are never observed as being homozygous asymptotes. b Rate of homozygosity, which is the percentage of individuals that are homozygous for any haplotype, is high for small window sizes but quickly declines. The assumption that phased marker homozygosity implies identity by descent underlies the population frequency and patrio tests for haplotype lethality
