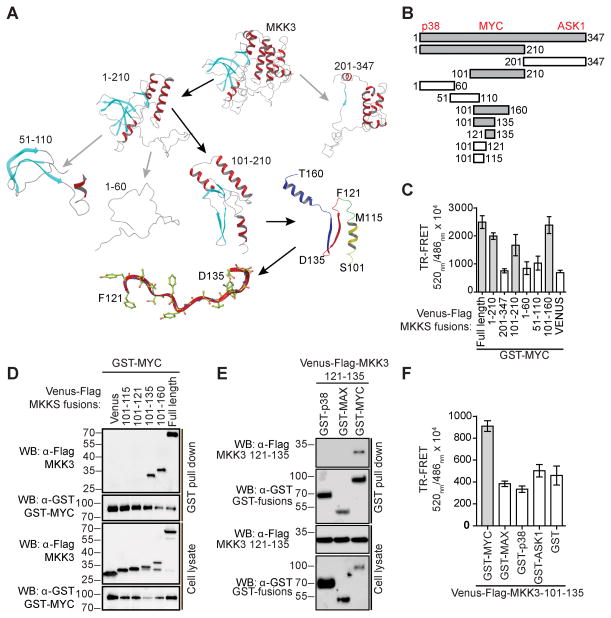
Figure 5. MKK3 121–135 is sufficient for MYC-binding.
A) A computational model of MKK3 was utilized to guide the design of truncation fragments. MKK3 MYC-binding fragments are highlighted with black arrows. B) MKK3 fragments were generated to identify MKK3 binding site for MYC. MKK3 MYC-binding regions are shown in grey. Approximate locations of MKK3 sites for p38, ASK1, and MYC are indicated on top. C) Interaction of MYC with fragments of MKK3 in a TR-FRET assay in HEK293T cells. The bars represent average TR-FRET signals measured in triplicate. D) Interaction of MYC with defined peptides of MKK3 in a GST-pull down assay performed in HEK293T cells. E) Interaction of MKK3 121–135 peptide with MYC in a GST-pull down assay in HEK293T cells with p38 and MAX as controls. F) MKK3 101–135 showed selective interaction with MYC in a TR-FRET assay.