Figure 2.
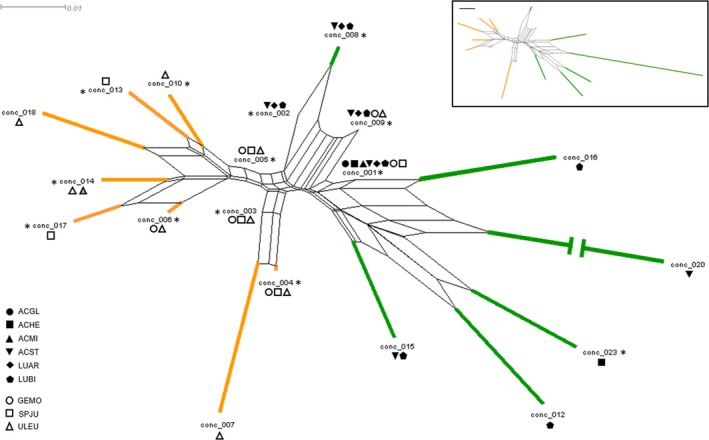
Wild‐grown invasive and native legumes associate with distinct communities of rhizobia. Neighbor‐net diagram depicting the network of operational taxonomic units sharing 98% sequence identity across concatenated ITS and nifD sequences for the 715 Bradyrhizobium isolates characterized in this study. Line color indicates genotypes associated with either native (green) or invasive (orange) legumes. Shapes indicate the legume species with which each genotype associated and whether the legume was native (black‐filled shapes) or invasive (open shapes). The gray‐filled triangle depicts the concatenated genotype of the one isolate identified from U. europaeus in its native range (Portugal). Asterisks indicate genotypes used in the greenhouse nodulation assay. ACGL, Acmispon glaber, ACHE, A. heermannii, ACMI, A. micranthus, ACST, A. strigosus, LUAR, Lupinus arboreous, LUBI, L. bicolor, GEMO, Genista monspessulana, SPJU, Spartium junceum, ULEU, Ulex europaeus
