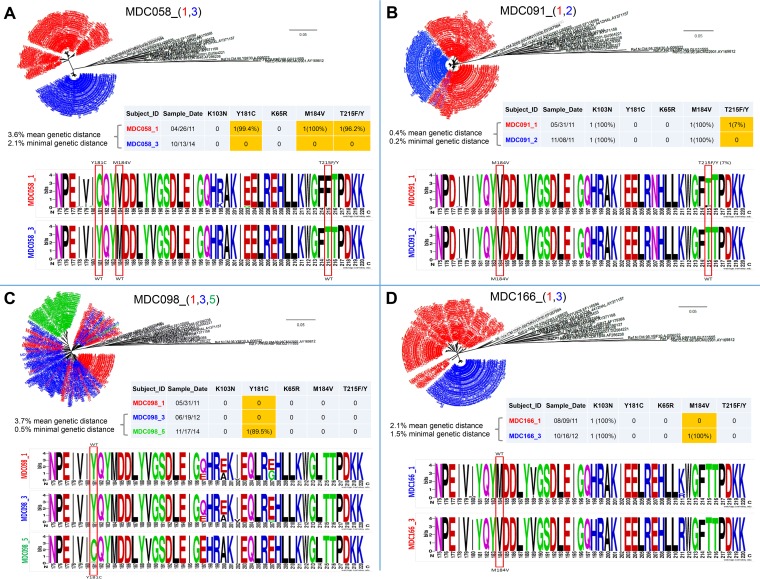
FIG 3.
Phylogenetic and sequence analysis of study subjects with longitudinal changes in drug resistance mutations in the absence of superinfection. Longitudinal changes in HIV drug resistance (HIVDR) mutations were observed for the four study subjects MDC058 (A), MDC091 (B), MDC098 (C), and MDC166 (D). Using the NGS pol sequences, a multi-time-point phylogenetic tree (top), a drug resistance pattern and genetic distance analysis (middle), and a sequence logo analysis (bottom) were performed for each study subject. (Top) Phylogenetic trees were generated using the MEGA (neighbor-joining method) and FigTree softwares. Sequences in black are references downloaded from the HIV sequence database (https://www.hiv.lanl.gov). Numbers in parentheses after the patient IDs and a low dash indicate the sampling time points, and the corresponding sequences are shown with the same colors in the phylogenetic tree. The bar indicates the genetic distance. (Middle) Table with drug resistance patterns for each time point. Discordant longitudinal HIVDR mutations are highlighted in yellow. Mean genetic distances between time points and minimal genetic distances between two NGS sequences from different time points (in percentages) were calculated in MEGA. (Bottom) Sequence logo analysis was performed with the WebLogo online tool (weblogo.berkeley.edu). The red rectangles indicate the presence of HIVDR mutations with/without longitudinal change. The analysis was performed from amino acid positions 175 to 220 of the product of the rt gene and includes all mutations of interest. (A) MDC058 changed from mutant types C, V, and Fs to wild-type Y, M, and T at positions 181, 184, and 215, respectively. The changes in the rt sequences occurred between time points 1 and 3 within 42 months. (B) MDC091 changed from mutant type F (7% prevalence) to wild-type T at position 215. The changes in the rt sequences occurred between time points 1 and 2 within 6 months. (C) MDC098 changed from wild-type Y to mutant type C at position 181. The changes in rt sequences occurred between time points 3 and 5 within 17 months. (D) MDC166 changed from wild-type M to mutant type V at position 184. The changes in the rt sequences occurred between time points 1 and 3 within 14 months.