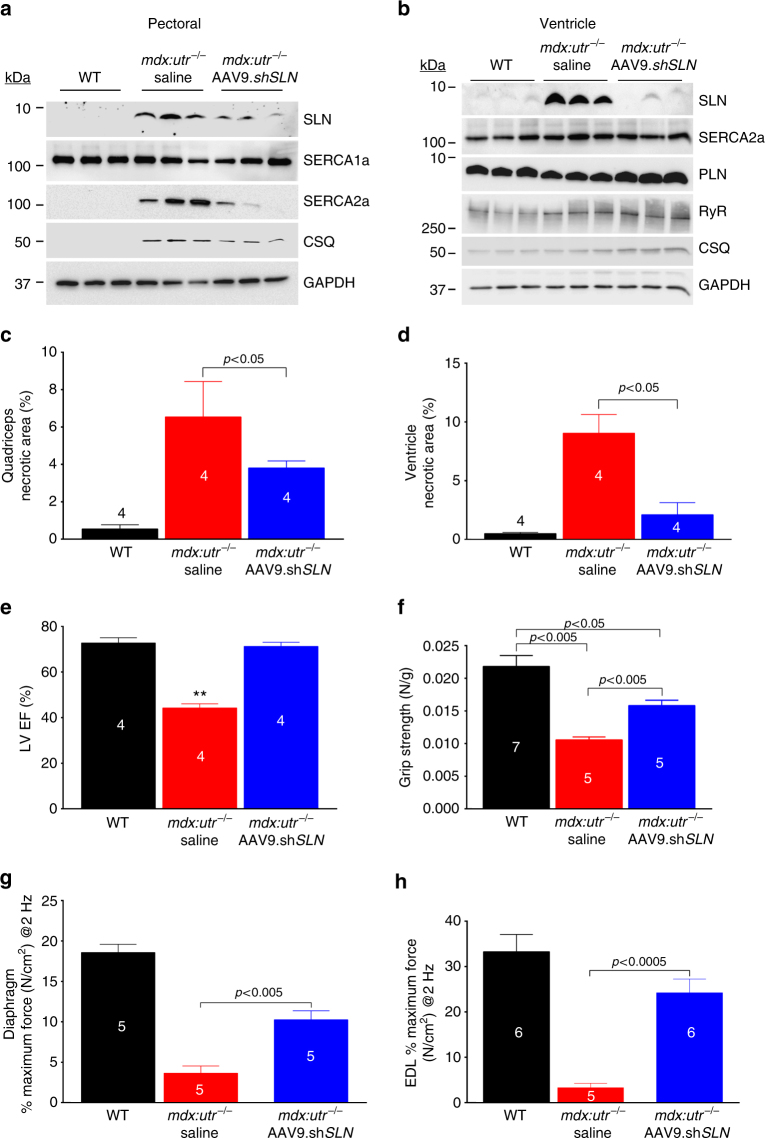
Fig. 6.
Postnatal AAV9.shSLN treatment ameliorates DMD and associated cardiomyopathy in mdx:utr −/− mice. 1-month old male and female mice are injected with AAV or saline and experiments are performed 12 weeks post-injection. a, b Representative western blots show that AAV9.shSLN treatment effectively reduces SLN expression in skeletal (pectoral muscle) and cardiac (ventricle) muscles. Uncropped scans of western blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8d, e. The AAV treatment reduced SERCA2a and CSQ levels in the pectoral muscles of mdx:utr −/− mice. c, d Quantitation of areas with mononuclear infiltration in the H&E stained tissue sections show that cell necrosis is significantly reduced in both quadriceps and ventricles of AAV treated mdx:utr −/− mice compared to that of saline injected mdx:utr −/− controls. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. The n number for each group and the p values (t-test with Welch’s correction) are shown within the graph. e LV EF, f forelimb muscle strength, and g, h the maximum twitch force generated by EDL and hemidiaphragm at 2 Hz are significantly improved in the AAV treated mice compared to that of saline injected mdx:utr −/− controls. **p < 0.0001 vs. other groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. The n number for each group and the p values (t-test with Welch’s correction) are shown within the graph