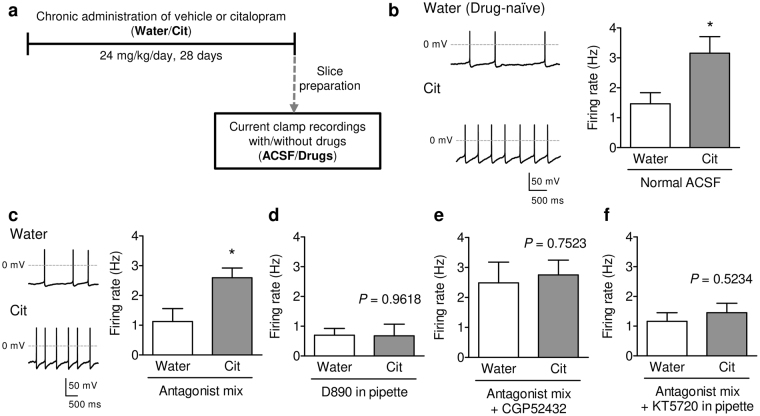
Figure 4.
Chronic administration of citalopram increased the spontaneous firing rate of DRN serotonergic neurons. (a) Outline of recordings from citalopram-administrated mice. After chronic treatment with citalopram (Cit; 24 mg/kg/day) or its vehicle (Water) for 28 days, acute raphe slices were prepared, and whole-cell current clamp recordings were performed. (b) Representative traces (left) and average spontaneous firing rate (right) of DRN serotonergic neurons from drug-naïve (Water) and citalopram-treated (Cit) mice. *P < 0.05 vs. Water. (Water, n = 8 neurons from 4 mice; Cit, n = 13 neurons from 4 mice; Student’s t-test; P = 0.0491). (c) Representative traces (left) and average spontaneous firing rate (right) of DRN serotonergic neurons in the presence of the antagonist mix (20 μM DNQX, 50 μM APV, 20 μM Bicuculline, 0.1 μM WAY100635, and 1 μM GR127935). *P < 0.05 vs. Water. (Water, n = 8 neurons from 3 mice; Cit, n = 8 neurons from 4 mice; Student’s t-test; P = 0.0168). (d) The effects of intracellularly applied D890 on the spontaneous firing rate of DRN serotonergic neurons. P = 0.9618 vs. Water by Student’s t-test, Water, n = 13 neurons from 2 mice; Cit, n = 10 neurons from 2 mice. (e) The spontaneous firing rate of DRN serotonergic neurons in the presence of the antagonist mix and CGP52432. P = 0.7523 vs. Water by Student’s t-test, Water, n = 9 neurons from 2 mice; Cit, n = 12 neurons from 2 mice. (f) The effects of intracellularly applied KT5720 on the spontaneous firing rate of DRN serotonergic neurons in the presence of the antagonist mix. P = 0.5234 vs. Water by Student’s t-test, Water, n = 16 neurons from 2 mice; Cit, n = 22 neurons from 2 mice. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.