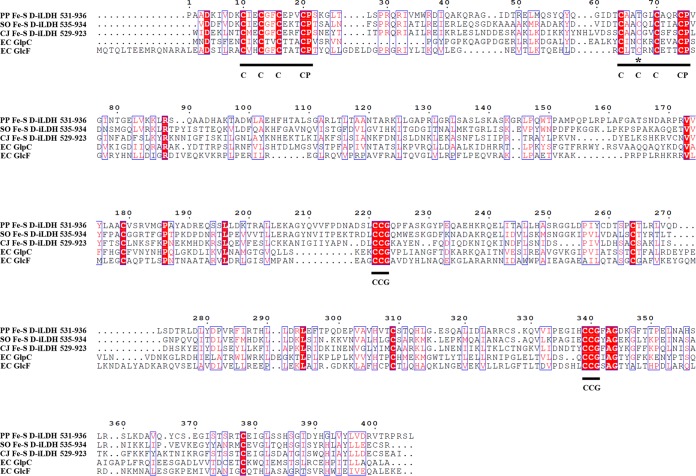
FIG 3.
Multiple-sequence alignment of Fe-S oxidoreductase domain of Fe-S d-iLDH and its homologs. PP Fe-S d-iLDH 531-936, predicted Fe-S oxidoreductase domain of Fe-S d-iLDH from P. putida KT2440 (accession no. AAN70309.1); SO Fe-S d-iLDH 535-934, predicted Fe-S oxidoreductase domain of Fe-S d-iLDH from S. oneidensis MR-1 (accession no. AAN54582.2); CJ Fe-S d-iLDH 529-923, predicted Fe-S oxidoreductase domain of Fe-S d-iLDH from C. jejuni NCTC 11168 (accession no. CAL35682.1); EC GlpC, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase subunit C from E. coli (accession no. AAC75303.1); EC GlcF, glycolate oxidase subunit F from E. coli (accession no. AJE57532.1). Blue boxes indicate sites that have high similarities among the sequences. White letters indicate identical residues; red letters indicate that residues are not identical but belong to the same group (alkaline, acidic, nonpolar, or nonionizing polar amino acids) or that vacancies occur in some sequences, with residues in other sequences being identical or similar. The underlined regions are the consensus sequence of Fe-S cluster-binding sites (C, cysteine; P, proline; G, glycine), and the asterisks indicates the sites that do not accord with the consensus sequence.