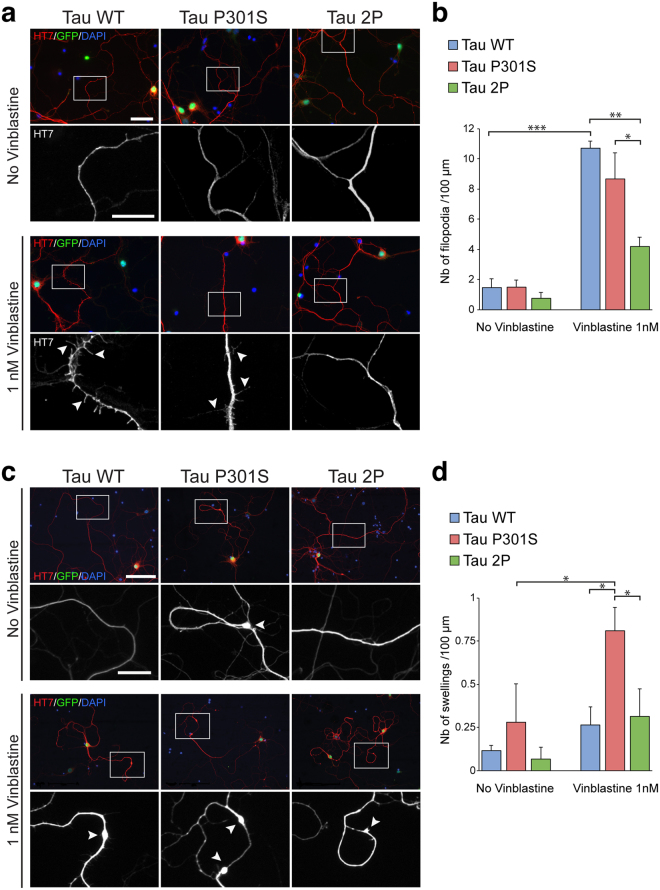
Figure 7.
2P-modified tau has protective effects on the microtubule network in primary cortical neurons exposed to vinblastine. Overexpression of Tau 2P prevents the formation of filopodia in mouse cortical neurons exposed to vinblastine. (a) Immunodetection of human tau (HT7) and GFP in cortical neurons (DIV5) infected with a bicistronic AAV-GFP/tau vector to overexpress each of the different human tau variants (WT, P301S or 2P). Nuclear expression of GFP is used to identify the transduced neurons. Upper panels show representative images of neurons in the control condition. Lower panels show cortical neurons after 24 h exposure to 1 nM vinblastine. Arrowheads indicate the presence of filopodia on the neuronal processes. Scale bars: 40 µm and 20 µm (lower panels). (b) Quantification of the number of filopodia normalized to neurite length. Exposure to 1 nM vinblastine increases the number of filopodia. Note that the overexpression of 2P tau significantly reduces the number of neuritic filopodia compared to WT and P301S tau. (c) Seven days exposure to 1 nM vinblastine leads to the formation of neuritic swellings. Experimental conditions and immunodetection are similar to panel (a). Lower panels show higher magnification of HT7 immunostaining in the neurites of neurons overexpressing human tau. Arrowheads indicate the presence of neuritic swellings. Scale bars: 100 µm and 20 µm (lower panels). (d) Quantification of the number of swellings normalized to neurite length. Exposure to 1 nM vinblastine increases the number of swellings in neurons overexpressing P301S tau. For all conditions: n = 3. Statistical analysis: two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s (b) or Fisher’s LSD (d) post-hoc tests, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.