FIG 1.
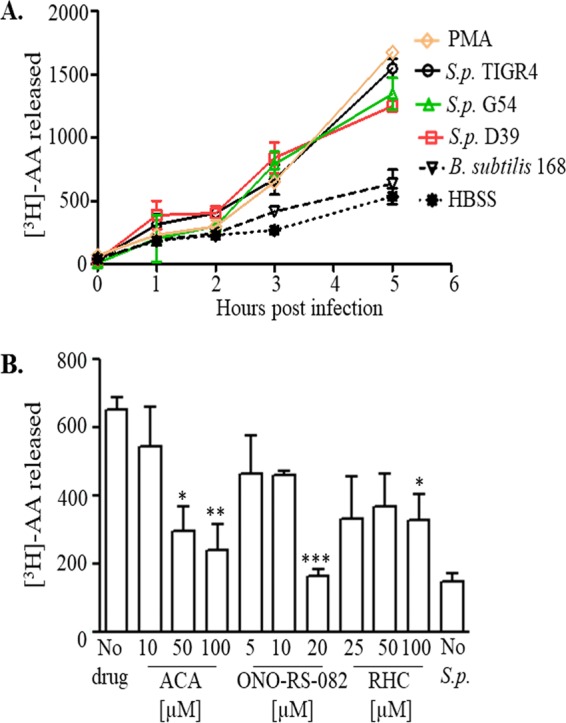
S. pneumoniae infection of airway epithelial cells triggers arachidonic acid (AA) release. (A) H292 cell monolayers were labeled with [3H]AA as detailed in Materials and Methods and infected with the indicated S. pneumoniae (S.p.) strains (each of a different capsular serotype) or with B. subtilis strain 168 at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 (1 ×107 CFU/monolayer). Supernatants were collected at the indicated times postinfection, and radioactive counts released into the supernatants were measured by scintillation counting. Labeled H292 cell monolayers treated with PMA and HBSS+Ca/Mg were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Shown are results from a representative of two experiments. (B) H292 cell monolayers labeled with [3H]AA were treated with the indicated concentrations of pan-PLA2 inhibitors ACA or ONO-RS-082 or the DAG lipase inhibitor RHC-80267 (labeled as RHC) prior to infection with S. pneumoniae TIGR4, as detailed in Materials and Methods. Labeled H292 cell monolayers treated with HBSS+Ca/Mg were used as negative controls. Radioactive counts released into supernatants were determined by scintillation counting. Shown are results from a representative of three experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (compared with the no-drug control, using one-way ANOVA).
