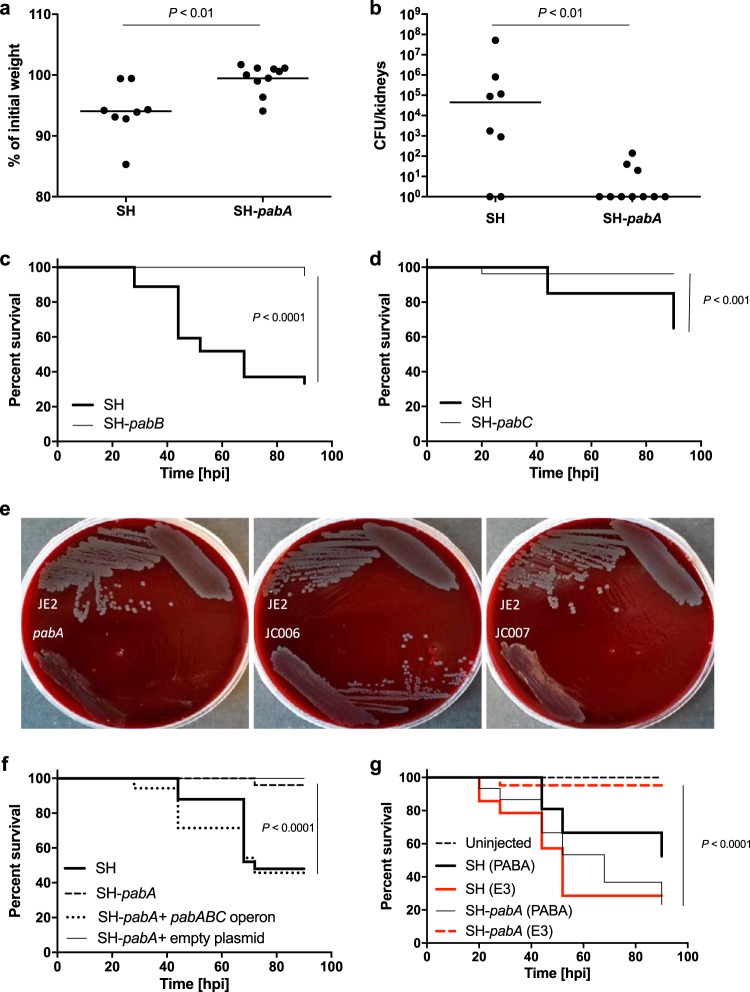
FIG 3.
The pabABC operon is required for pathogenesis. (a and b) Female BALB/c mice (n = 10) were injected i.v. with 2 × 107 CFU S. aureus SH1000 (SH) or 4 × 107 CFU S. aureus SH1000 pabA (SH-pabA). Weight loss (a) and CFU counts in the kidneys (b) were measured after 3 days. (c) Survival curves of fish injected with S. aureus SH1000 (1,500 CFU) or S. aureus SH1000 pabB. (d) Survival curves of fish injected with S. aureus SH1000 (1,500 CFU) or S. aureus SH1000 pabC. (e) Growth of the parent strain (JE2), the pabA mutant, the genetically complemented pabA strain (with pJC002 integrated) (strain JC006), or a control integrated strain (with the empty pKASBAR plasmid in the pabA mutant) (strain JC007) on unsupplemented human blood agar (30%, vol/vol). Plates were incubated aerobically at 37°C for 48 h. (f) Survival curves of fish injected with 1,500 CFU of S. aureus SH1000, S. aureus SH1000 pabA, S. aureus SH1000 pabA plus the pabABC operon (with pJC002 integrated) (strain JC010), or S. aureus SH1000 pabA with an empty plasmid only (pKASBAR) (strain JC011). (g) Survival curves of fish injected with 1,500 CFU of S. aureus SH1000 or S. aureus SH1000 pabA followed by immediate immersion in either unsupplemented E3 medium (red) or E3 medium supplemented with 7 μg ml−1 PABA (black). Uninjected fish were included as controls under each condition.