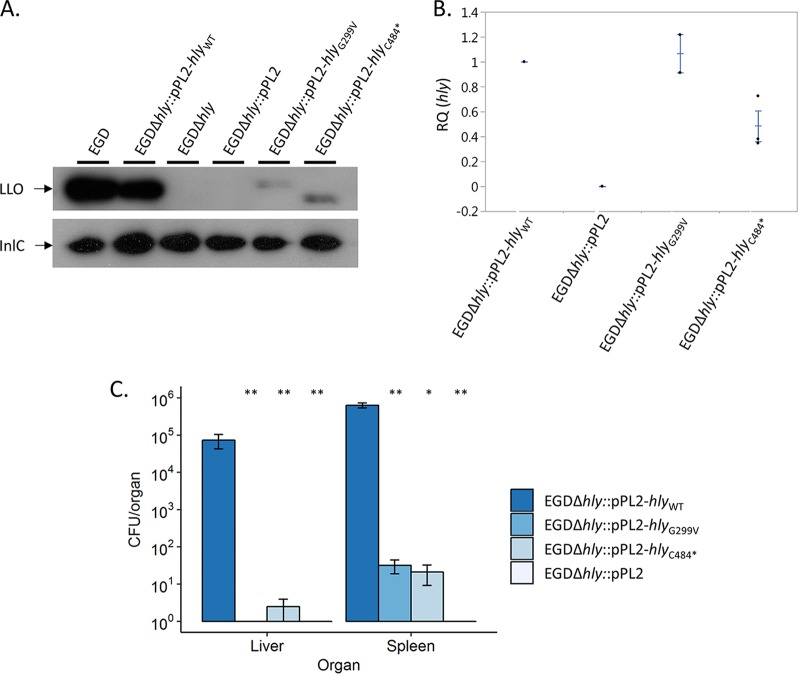
FIG 3.
Characterization of the G299V substitution in LLO and the truncated LLO at position 484. (A) Western blotting of the culture supernatants of EGD and EGDΔhly complemented or not with the pPL2 plasmid alone or containing the hlyWT, hlyG299V, or hlyC484* gene. LLO detection was performed by using LLO-specific antibodies, and InlC-specific antibodies were used as loading controls. (B) qRT-PCR quantification of hly transcripts produced in BHI broth at 37°C by the EGDΔhly strain complemented with the pPL2 plasmid alone or containing the hlyWT, hlyG299V, or hlyC484* gene. Each strain was tested at least three times using independent precultures. gyrB was used as a stable reference gene for normalization. Results are shown as fold change of hly expression relative to that in EGD (RQ, relative quantities). Each central bar represents the mean of at least three replications. Error bars indicate standard deviations from the means. (C) In vivo characterization of the hlyG299V and hlyC484* mutant strains compared to the hlyWT strain. Each BALB/c mouse was infected intravenously with 1 × 104 CFU. Animals were sacrificed 72 h after infection. Numbers of CFU per organ are shown for all tested strains. No bacteria could be recovered from the liver of mice infected with the EGDΔhly::pPL2-hlyG299V and EGDΔhly::pPL2 strains or from the spleen of mice infected with EGDΔhly::pPL2. Statistical analyses were performed with the Mann-Whitney U test, by comparing results with those of EGDΔhly::pPL2-hlyWT. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.