FIG 4.
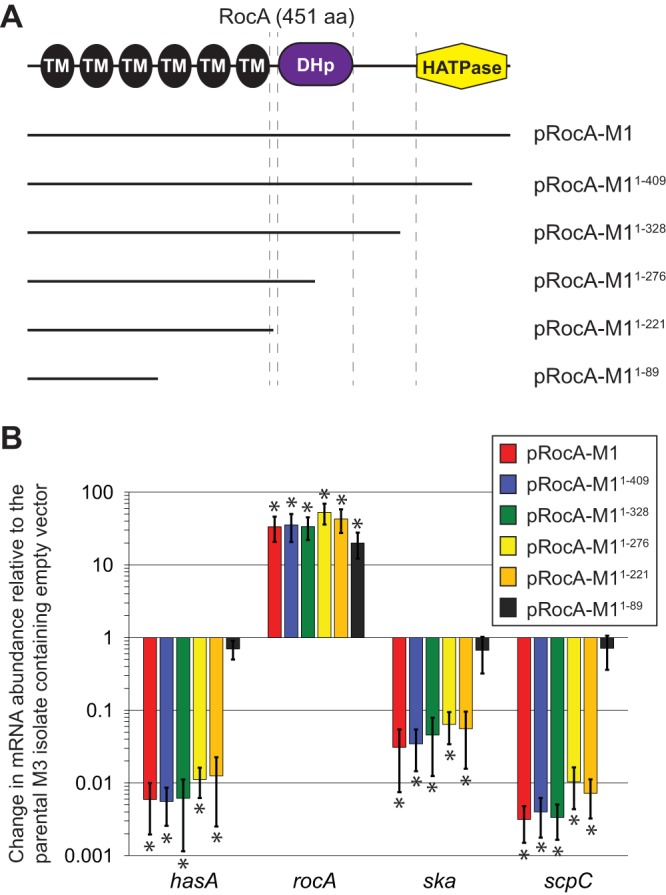
Overexpression of the membrane-spanning domains of RocA is sufficient for regulatory activity. (A) Schematic of the RocA protein and of the extent of RocA truncations within a series of constructed plasmids. (B) TaqMan-based quantitative RT-PCR analysis of rocA and select (hasA, ska, and scpC) RocA-regulated mRNA abundances. Derivatives of the naturally rocA mutant M3 isolate MGAS10870 containing the plasmids shown in panel A were compared to the same strain containing empty vector. Shown are the averages (±standard deviations) of triplicate samples run in duplicate. The asterisks highlight statistical significance relative to the parental M3 isolate containing empty vector (t test; *, P < 0.001).
