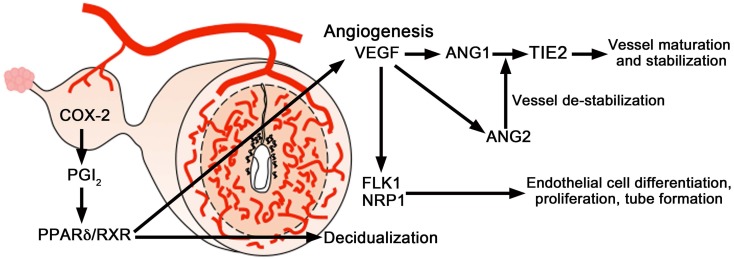
Fig. 4.
A schematic diagram of angiogenic signaling in the uterus during implantation. COX2-derived prostaglandins are important for uterine angiogenesis during implantation and decidualization and primarily target the VEGF system, but not the angiopoietin system. The proangiogenic factor VEGF and its receptor FLK1 are important for uterine angiogenesis during the post-implantation period. VEGF in complementation with the angiopoietins (ANG1 and ANG2) and their receptor TIE2 directs angiogenesis during decidualization. ANG1 in collaboration with VEGF induces vessel maturation and maintains vessel leakiness, whereas ANG2 induces vessel destabilization required for further sprouting in the presence of VEGF.