Figure 2.
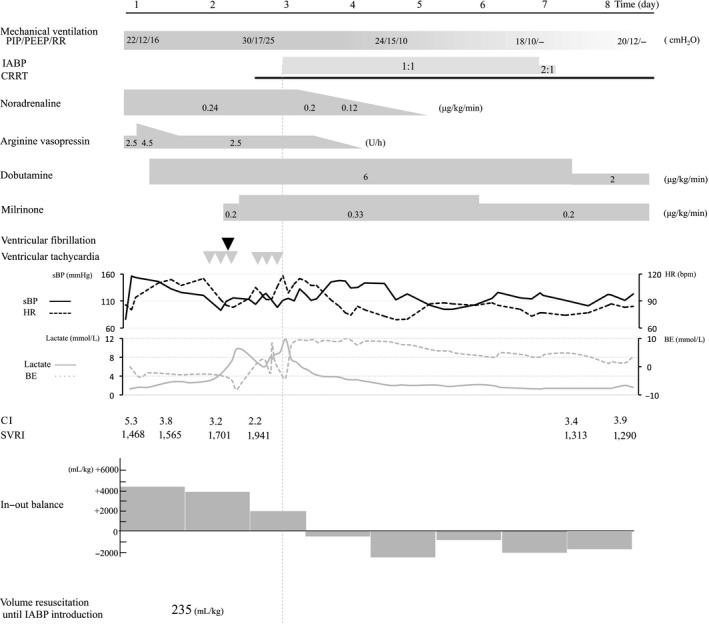
Clinical course from day 1 to 8 in a 62‐year‐old man with severe septic cardiomyopathy. Top panel, ventilator settings (mode, positive end‐expiratory pressure [PEEP], peak inspiratory pressure [PIP], and respiratory rate [RR]), duration of intra‐aortic balloon pump (IABP) use, continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), and direct hemoperfusion with a polymyxin B immobilized fiber column (PMX). Middle panel, catecholamine dose. Bottom panel, change in vital signs (systolic blood pressure [sBP] is shown by the solid black line; heart rate [HR] is shown by the broken black line), lactate level (solid gray line), base excess (BE; broken gray line), cardiac index (CI), systemic circulation resistance index (SVRI), and fluid balance. Gray and black triangles show the points when ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia occurred, respectively.
