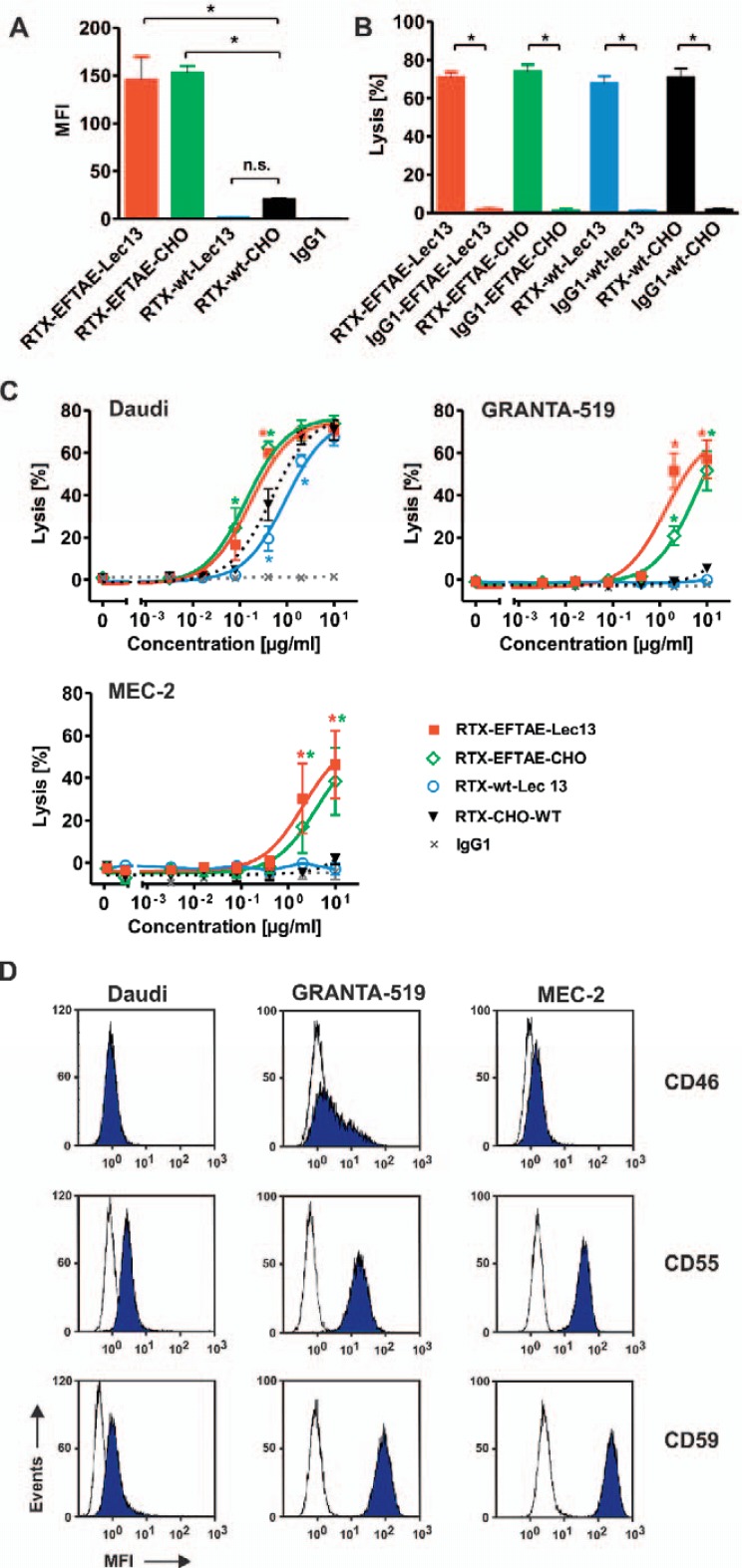
Fig. 3.
Induction of CDC by rituximab antibody variants. A Daudi cells were coated with RTX-wt-CHO, RTX-EFTAE-CHO, RTX-wt-Lec13 or RTX-EFTAE-Lec13 (concentration: 50 µg/ml) and then incubated in the presence of human serum (1%) as a source of C1q. Eculizumab was added to block CDC. Deposition of C1q was analyzed with a FITC-coupled mouse anti-human C1q antibody by flow cytometry. Bars represent mean values ± SEM (n = 3). B CDC by rituximab variants in comparison to corresponding HER2-specific control antibodies was analyzed by 51Cr release experiments using Daudi cells as targets in the presence of 25% human plasma. Antibodies were applied at 10 µg/ml. Mean values ± SEM are depicted. Significant differences between CD20 antibodies and similarly designed control proteins are indicated (*, p ≤ 0.05; n = 3). C Dose-dependent induction of CDC against Daudi (n = 3), GRANTA-519 (n = 4) and MEC-2 (n = 4) cells by rituximab variants. Human plasma (25%) was added as a source of complement. Statistically significant differences in CDC between engineered antibodies and the native CD20 IgG1 molecule are indicated (*, P ≤ 0.05). D Daudi, GRANTA-519 and MEC-2 cells were incubated with specific antibodies against mCRPs CD46, CD55 or CD59 (blue peaks) or isotype matched control antibodies (white peaks), which were subsequently detected with secondary FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG Fc F(ab')2 fragments, and expression levels were analyzed by flow cytometry. Results from one representative experiment are shown (n = 3; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity).