Figure 4.
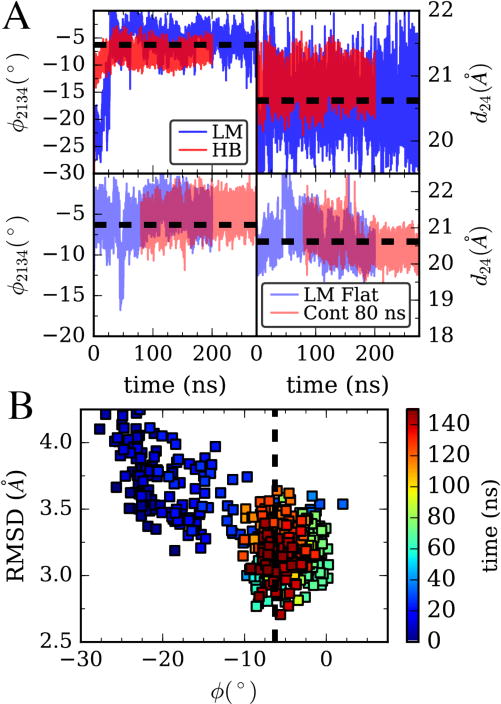
(A) Top, Adaptive Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) algorithm matching 4 CVs: cleft distance, twist angle, and their second moments is compared to harmonic bias on angle and distance with large spring constants on both. Data is for all-atom MD simulations of the G/monomer system in Figure 1. Bottom, in blue, the LM algorithm is performed on an actin monomer starting from a filament structure (F/monomer in Figure 1). In red, the bias parameters at time 80 ns are fixed and a separate simulation is run using this learned bias. (B) Comparison of the structure of the G/monomer in the LM trajectory from (A,top) with a filament subunit by backbone RMSD. Color shows progress along the trajectory in (A).
