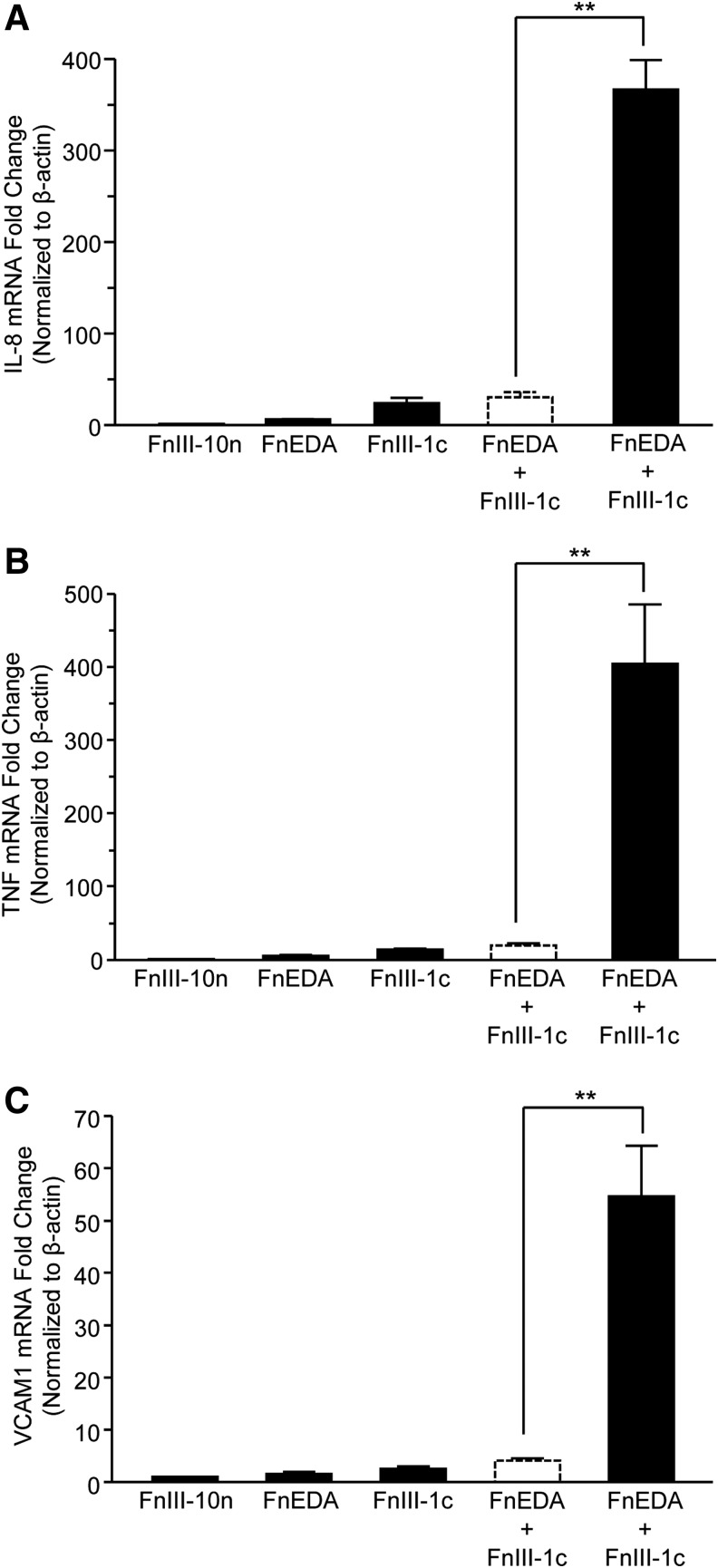
Figure 1.
FnIII-1c and FnEDA modules stimulate a synergistic increase in the expression of fibro-inflammatory genes. Confluent monolayers of human dermal fibroblasts were serum starved overnight; then, they were treated with 2 μM each of FnIII domains, alone and in combination. Data are presented as fold increase over the control module, FnIII-10n, which was set at 1. The theoretical expected additive effect of combining FnEDA and FnIII-1c is represented by the open dashed line bar. After a 2 h incubation period, mRNA was isolated and analyzed via qRT-PCR by using primers to human IL-8 (A), TNF-α (B), and human VCAM-1 (C). Statistical analysis was performed by using a Student's t-test. **p < 0.01. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3). EDA, extra domain A; IL-8, interleukin 8; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; SEM, standard error of the mean.