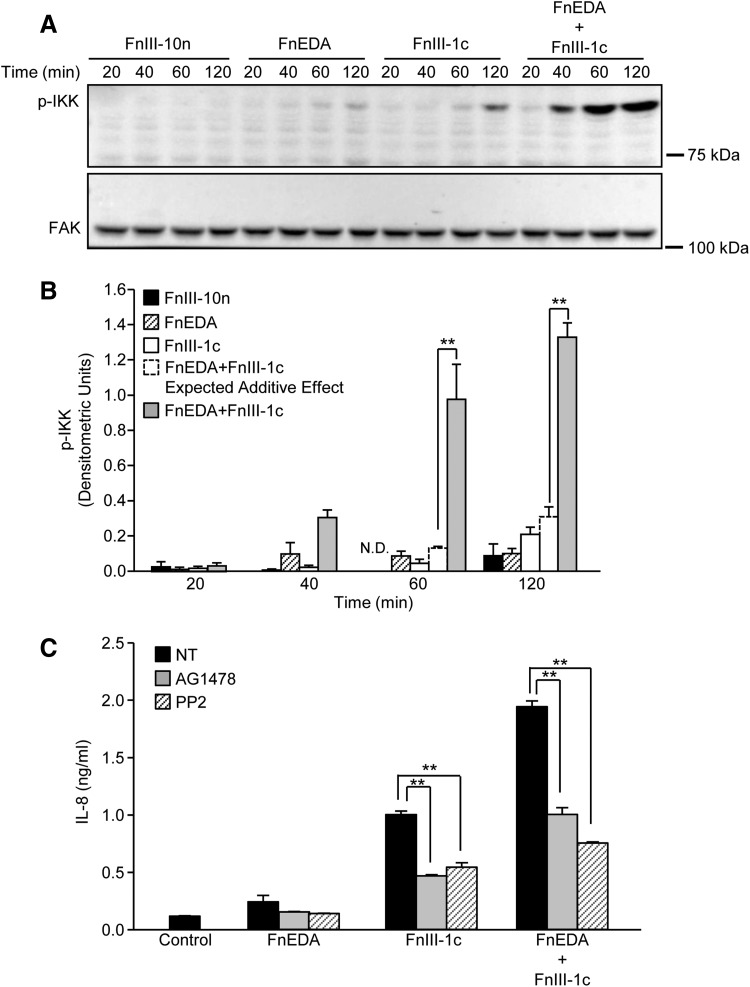
Figure 3.
FnIII-1c and FnEDA synergistically regulate IKK activation. Monolayers of human dermal fibroblasts were serum starved overnight; then, they were treated with the designated FnIII domains (2 μM), alone and in combination. At the indicated time, cells were lysed and phospho-IKK (pIKK) was assessed by Western blot. FAK served as a loading control (A). Blots were quantified by densitometry, and values for p-IKK were normalized to FAK. The theoretical expected additive effect of combining FnEDA and FnIII-1c is represented by the open dashed line bar at the 60 and 120 min time points. Graph represents the mean ± S.E.M. of three individual experiments (B). Statistical analysis was performed by using a Student's t-test. **p < 0.01. Fibroblasts were preincubated for 1 h with inhibitors to EGFR kinase, AG1478 (10 μM), Src kinase, PP2 (10 μM), or NT before incubation with the designated FnIII domains (4 μM), individually or in combination. Control cells received just buffer. After an additional 4 h, IL-8 in the conditioned medium was determined by ELISA (C). Statistical analysis was performed by using a Student's t-test. **p < 0.01. Data represent the mean ± S.E.M. of triplicate samples from one representative experiment. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; IKK, inhibitor of kappa B kinase; NT, not treated.