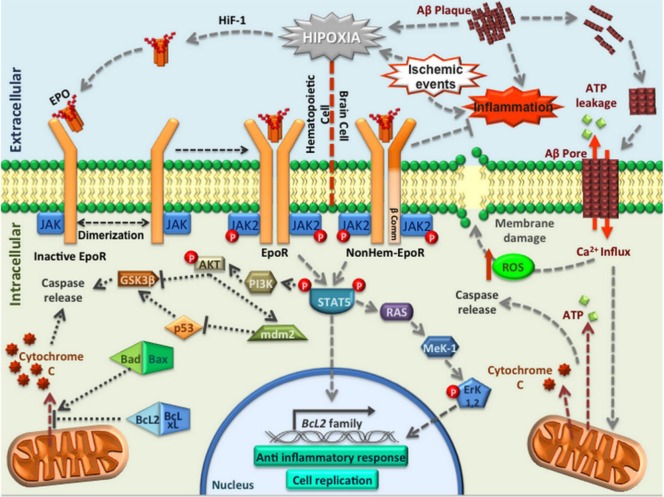
Figure 2.
Pathways involved in EpoR activation.
Principal signal pathways activated to induce neuroprotection when Epo interacts with EpoR or EpoRβ (expressed in CNS) in response to hypoxia or different types of stress, such as ischemic brain events or inflammation induced by Alzheimer′s disease. Epo or EPO: Erythropoietin; EpoR: Epo receptor; CNS: central nervous system; HiF-1: hypoxia inducible factor; Aβ: beta amyloid peptide; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; JAK: Janus kinase; ROS: reactive oxygen species; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; AKT: protein kinase B; PI3K: phosphoinositol 3′-kinase; STAT5: signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; MeK-1: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; Erk1,2: extracellular-regulated kinases 1,2; Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2; BclxL: B-cell lymphoma-extra large.