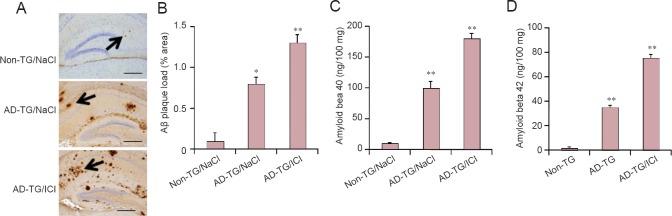
Figure 4.
Blocking beta 2-adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) increases amyloid beta (Aβ) accumulation in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 double transgenic (AD-TG) mice.
(A) Immunohistochemical staining of the hippocampus was performed 1 day after 5 days of training. The representative images show the levels of plaque load in the hippocampus of wild type control (non-TG), AD-TG/NaCl, and AD-TG/NaCl mice given ICI 118551 (AD-TG/ICI) immunostained with Aβ antibody under a light microscope. Results showed that ICI treatment of AD-TG mice increased Aβ accumulation in the hippocampus (indicated by arrow). Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Quantification of Aβ staining was performed by Image Pro Plus 6.0 software. (C and D) The levels of amyloid beta 40 (Aβ40) and amyloid beta 42 (Aβ42) in hippocampi were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. non-TG/NaCl. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 8, one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test). Wild type control (non-TG) and AD-TG mice were sub-grouped: saline control group, injections of 0.9% NaCl, termed non-TG/NaCl and AD-TG/NaCl; β2-AR antagonist treatment group, mice were administered ICI 118551 (1 mg/kg per day, intraperitoneally), termed AD-TG/ICI.