Figure 2. Total dietary sodium intake in deciles and multiple sclerosis risk in Nurses' Health Study (1984–2004) and Nurses' Health Study II (1991–2009).
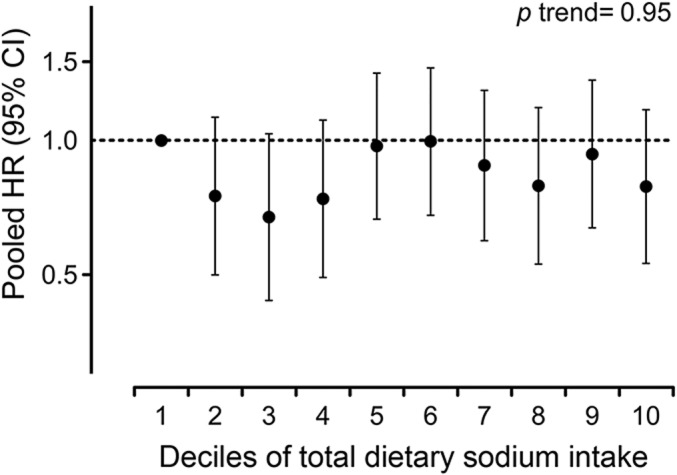
Total dietary sodium intake assessed by food frequency questionnaire at baseline was adjusted for energy intake using the residual method22 and subsequently calibrated using data from the Women's Lifestyle Validation Study.23,24 Pooled hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) adjusted for age, latitude of residence at age 15 (north, middle, south), ancestry (southern European, Scandinavian, other Caucasian, other), pack-years of smoking (0, <10, 10–24, ≥25), supplementary vitamin D intake (0, <400, ≥400 IU/d), body mass index at age 18 (<18.5, 18.5–<25, 25–<30, ≥30 kg/m2), and total energy intake.
