Figure 6. Potentiating interactions between post-PKC signaling pathways govern MMP1 gene induction.
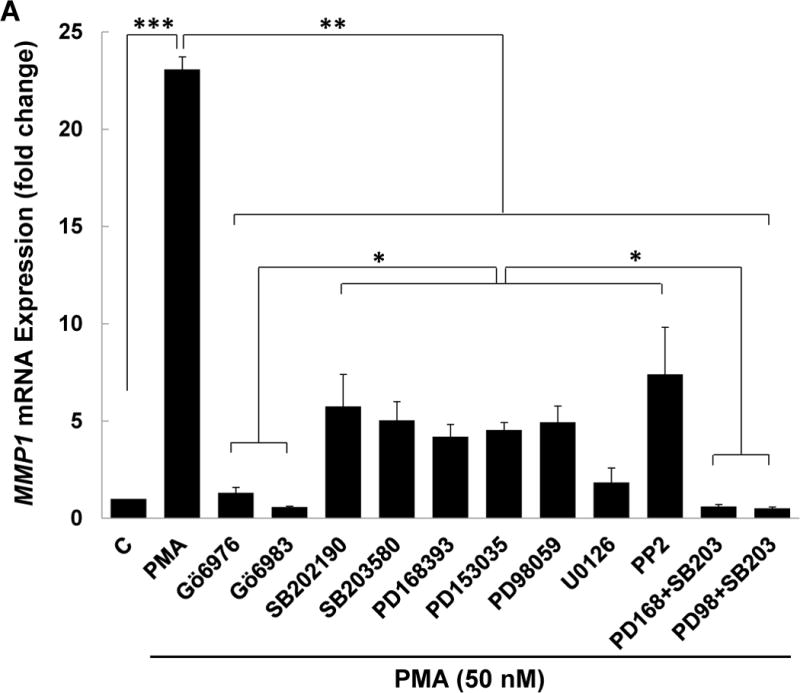
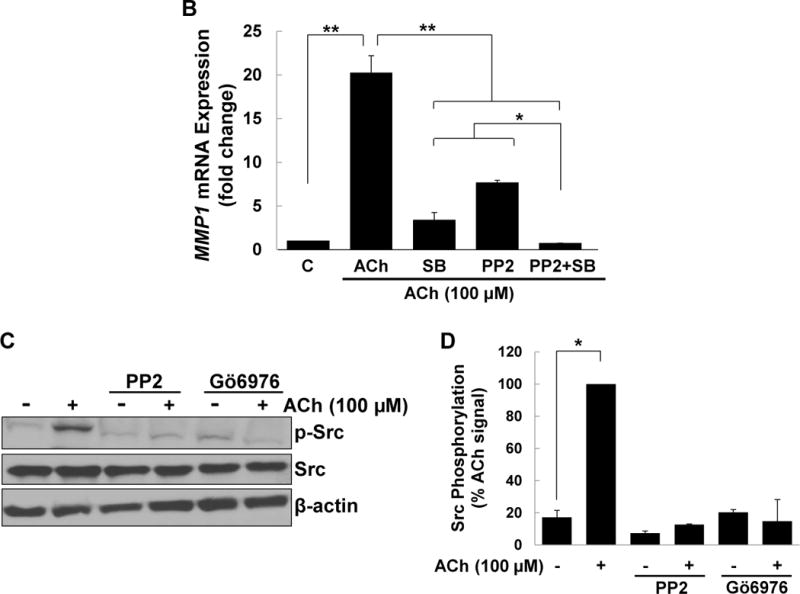
(A) HT-29 cells were pre-incubated for 45 min alone or with PKC-α/β1 inhibitors (5 μM Gӧ6976, 5 μM Gӧ6983), p38-α/β inhibitors (10 μM SB202190, 10 μM SB203580), EGFR inhibitors (5 μM PD168393, and PD153035), MEK inhibitors (10 μM PD98059, 10 μM U0126), or a Src inhibitor (10 μM PP2), alone or in combination, before adding 50 nM PMA for an additional 4-h incubation. MMP1 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR. PMA-induced MMP1 gene expression was abolished by pre-incubating cells with PKC-α/β1 inhibitors and attenuated by pre-incubating cells with inhibitors of p38-α/β, EGFR, MEK, and Src. Simultaneously blocking p38-α/β and EGFR, p38-α/β and MEK, or p38-α/β and Src abolished PMA-induced MMP1 gene expression. (B) HT-29 cells were pre-incubated for 45 min alone or with a p38-α/β (10 μM SB203580) or Src (10 μM PP2) inhibitor, alone or in combination, followed by an additional 4-h incubation with 100 μM ACh. MMP1 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR. ACh-induced MMP1 expression was attenuated by pre-incubation with p38-α/β and Src inhibitors and abolished by these inhibitors in combination. qPCR data were normalized to GAPDH and are the mean ± SE of three separate experiments. C, untreated control; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C) H508 cells were pre-incubated for 45 min with inhibitors of Src (10 μM PP2) and PKC-α/β1 (5 μM Gö6976) before adding ACh (100 μM) for an additional 5-min incubation. Cell extracts were immunoblotted with antibodies against phosphorylated and total Src. (D) Densitometry of immunoblots from two separate experiments shows ACh-induced Src phosphorylation was blocked by pre-incubating cells with Src and PKC-α/β1 inhibitors. *P < 0.05 compared to 100 μM ACh alone.
