Fig. 1.
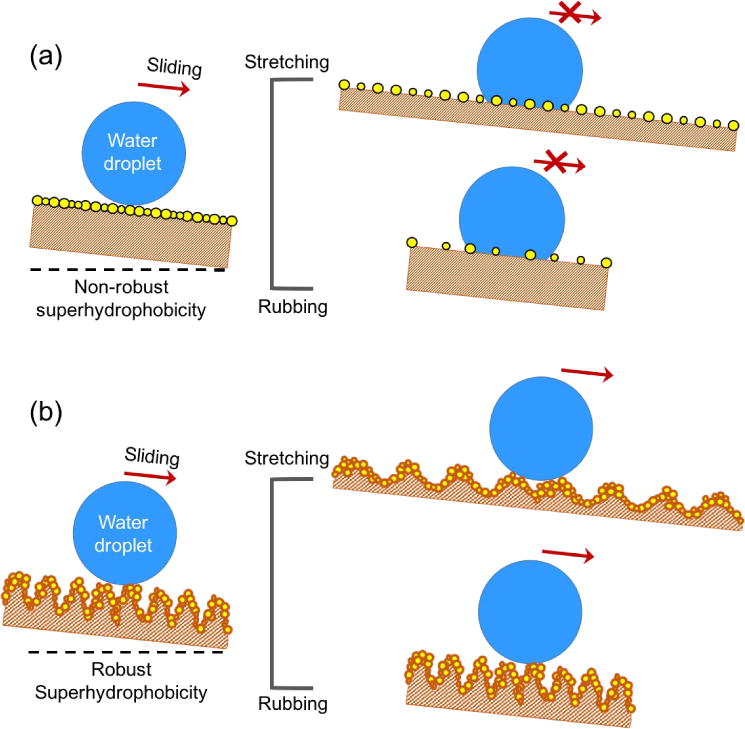
Structural comparison of the robust and conventional superhydrophobic surfaces. (a) Water droplet can slide off a lightly inclined freshly prepared non-robust superhydrophobic surface, while sticks to the surface if the surface receives stretching or rubbing due to increased particle distance and reduced surface roughness. (b) Water droplet slides off a lightly inclined robust superhydrophobic surface before and after stretching or rubbing process due to the preserved large surface roughness in both situations.
