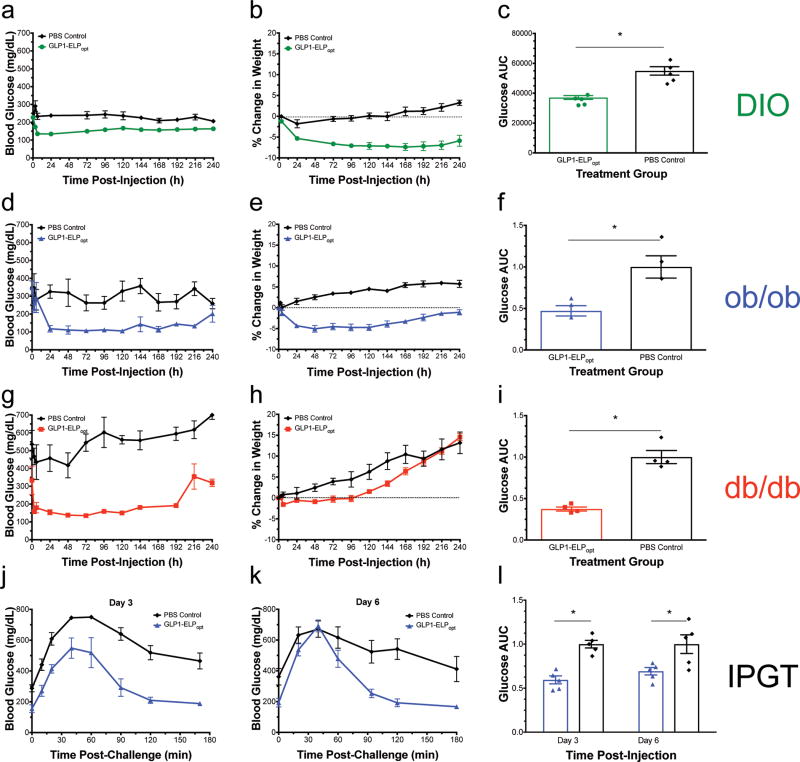
Figure 3. GLP1-ELP fusions were effective at controlling blood glucose levels for up to 10 days in 3 murine models of diabetes.
Blood glucose and percent weight change were monitored over 10 d after a single injection of either GLP1-ELPopt or an equivalent volume of PBS in DIO mice (n=5) (a–b), ob/ob mice (n=3) (d–e), and db/db mice (n=4) (g–h). Blood glucose AUC was calculated over 240 h and normalized within each experiment (by strain) to the PBS control group (c, f, and i). In the male ob/ob model (n=5), after a single injection, treated mice had an improved response to a 1g/kg glucose challenge compared to PBS controls on day 3 (j) and day 6 (k) post-injection. The normalized blood glucose AUC over 180 min is statistically significant at both time points (l). Symbol * indicated statistical significance of p<0.05. Data represent the mean and SEM.