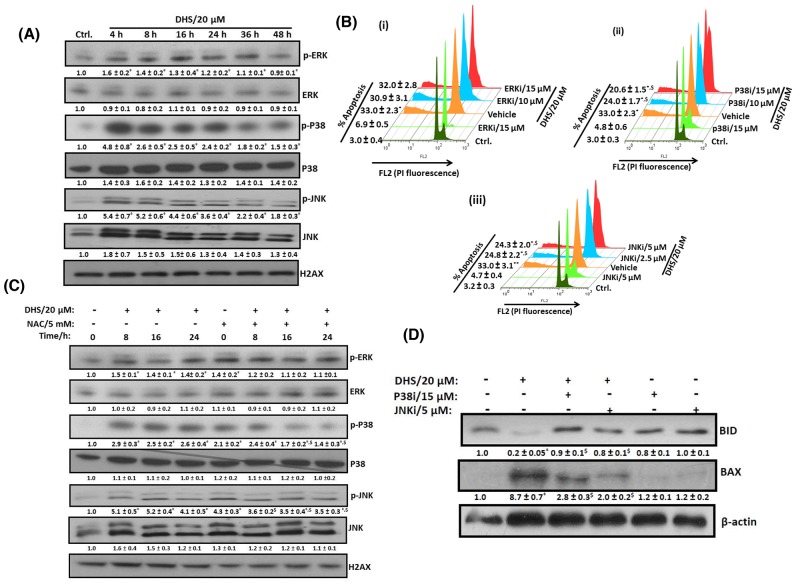
Figure 8. DHS-induced ROS activates p38 and JNK to modulate the BAX and BID levels and cause apoptosis in IMR32 cells.
(A) Activation of p38 and JNK by DHS. (B) Effects of specific MAPK inhibitors on apoptosis induction by DHS. (C) Effect of NAC on p38 and JNK activation by DHS. (D) Effect of p38 and JNK inhibitors on BAX expression and BIDcleavageby DHS. The cells were treated with DHS (0 and 20 μM) for different time periods and the MAPKs expressions analyzed by immunoblots. Similar experiments were also carried out by incubation with NAC (5 mM) for 1 h followed by treatment with DHS (0 and 20 μM) for different periods. The MAPKs phosphorylations and expressions in the cells treated with DHS (0 and 20 μM), NAC alone or in combination were analyzed by immunoblots. The sub-G1 populations of the cells treated with DHS (0 and 20 μM), the MAPKs inhibitors alone or in combination were analyzed by flow cytometry at 48 h, and the BAX and BID expressions analyzed by immunoblots. The whole cell extracts were used for all the immunoblots. The protein bands were detected using a Kodak Gel-doc software and the intensity ratios of the individual bands to that of vehicle control, taken as 1 (arbitrary unit) were quantified after normalizing with respective loading controls. All the determinations were made in duplicates for immunoblots and five replicates for flow cytometry analyses in 3-4 different experiments. The values are mean ± S. E. M. *p<0.05 compared to vehicle control; $p<0.05 compared to respective DHS treatments. Representative images and histograms are shown.