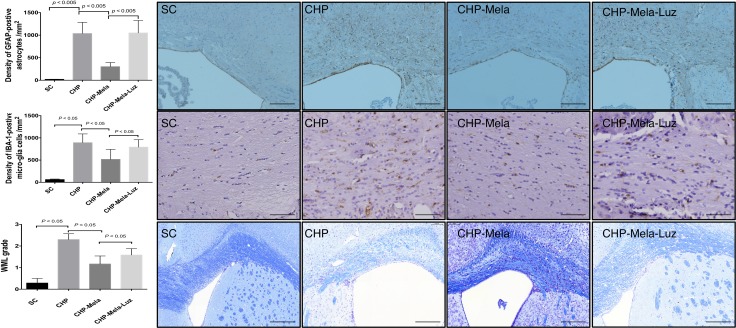
Figure 3.
Effects of Melatonin on the activation of astrocytes (A) microglia (B) and white matter lesion (C) in mice with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Upper panels: are representative photomicrographs of immunostaining of glial fibrillary acidic protein(GAFA) in the paramedian parts of the corpus callosum. Density of GFAP-positive astrocytes; Scale bar = 200 um. Middle panels: are representative photomicrographs of immunostaining of ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule-1 (IBA-1)-positive microglial cells in the paramedian parts of the corpus callosum. Density of Iba-1-positive microglial cells; Scale bar = 100 um. Lower panel: Immunohistochemical (IHC) images (100×) illustrating white matter lesion (WML) of different severity reflected in the grading; Scale bars in right lower corner represent 200 µm. All statistical analyses using one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison post hoc test. SC = sham control; CHP = cerebral hypoperfusion; CHP-Mela = cerebral hypoperfusion with melatonin (10mg/kg/day,ip); CHP-Mela-Luz = cerebral hypoperfusion with melatonin (10 mg/kg/day,ip) and luzindole (30 mg/kg,ip).