Figure 3. BPIS suppressed LPS-induced NF-κB expression by reduced phosphorylation of Akt in HT-29 cells.
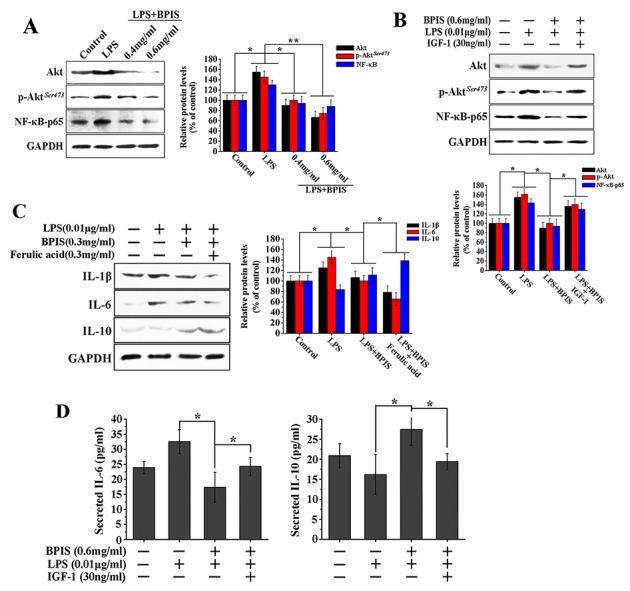
(A) HT-29 cells were treated for 24 h with 0.01 μg/ml LPS alone or together with various concentrations of BPIS (0.4 mg/ml and 0.6 mg/ml). The expression levels of total Akt, p-Akt and NF-κB-p65 were measured by western blot. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n=3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01). (B) The cells untreated and treated 0.01 μg/ml LPS alone or treated by adding LPS with 0.6 mg/ml BPIS and 30 ng/ml IGF-1 (Akt activator). The protein expression levels of total Akt, p-Akt and NF-κB-p65 were measured by western blot. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n=3, *p<0.05,). (C) The cells untreated and treated 0.01 μg/ml LPS alone or treated by adding LPS with 0.3 mg/ml BPIS and 0.3mg/ml ferulic acid. The protein expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 were measured by western blot. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n=3, *p<0.05). (D) HT-29 cells untreated and treated with 0.01 ng/ml LPS alone or treated by adding LPS with 0.6 mg/ml BPIS and 30 ng/ml IGF-1 (Akt activator). The levels of secreted IL-6 and IL-10 at 24 h in the cell culture medium were analyzed by ELISA. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4, * p < 0.05).
