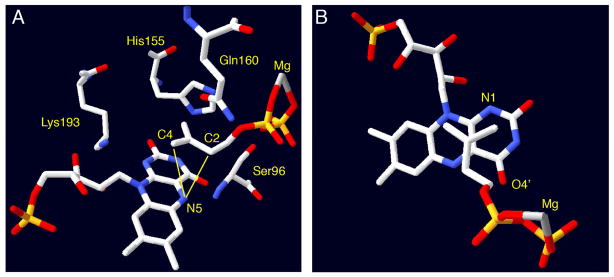
Figure 3.
Active site views of IDI-2 from Sulfolobus shibatae (PDB ID 2ZRY). Panel A shows the constellation of conserved amino acid residues in the immediate vicinity of the flavin and bound isoprene. Mutations of these residues perturb IDI-2 catalysis, but none of them are suitably positioned to mediate proton transfers to and from IPP. In contrast, the flavin N5 atom appears to be optimally positioned to both C2 (3.19 Å) and C4 (3.52 Å) to mediate the suprafacial 1,3-proton addition/elimination suggested by stereochemical studies. Panel B shows an alternative view of the same structure to illustrate the putative π-stacking between the flavin and isoprene. The flavin N1 and O4′ are also in the vicinity of IPP C4 and C2, respectively. Roles for these residues in catalysis cannot yet be ruled out, but they are not positioned as optimally as N5.