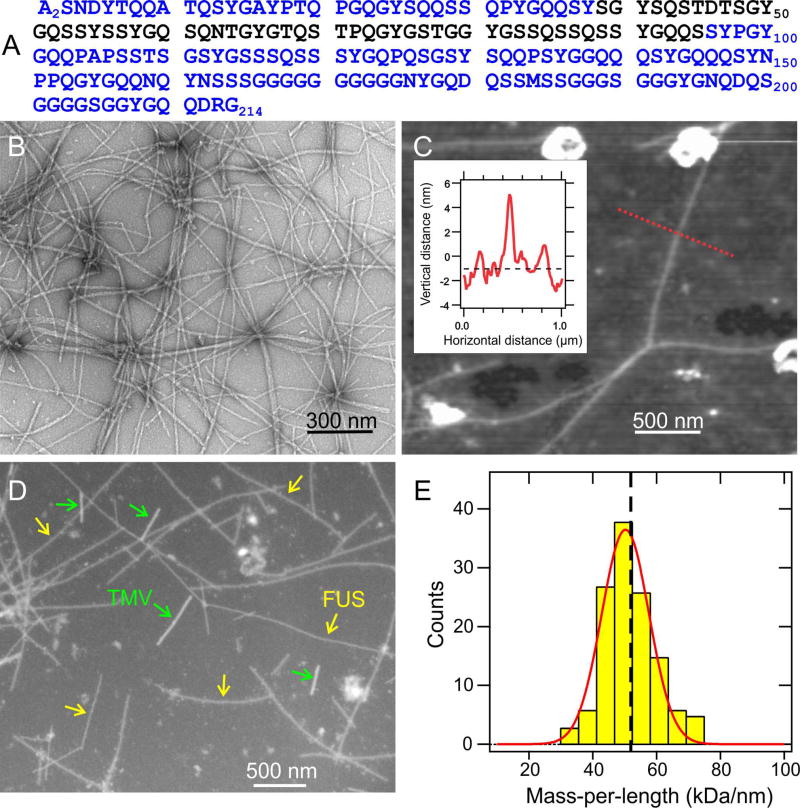
Fig. 1. Fibril formation by the low-complexity domain of FUS.
(A) Human FUS-LC sequence. Experiments were performed on samples with an additional N-terminal His tag, bearing the sequence MSYYHHHHHHDYDIPTTENLYFQGAMDP. (B) TEM image of negatively-stained FUS-LC fibrils. (C) AFM image of FUS-LC fibrils adsorbed to mica, with fibril heights indicating diameters of 5.5 ± 0.7 nm. Inset shows the height profile along the dotted red line. (D) Dark-field TEM image of unstained FUS-LC fibrils. Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) particles are included as mass-per-length (MPL) standards for image intensity calibration. (E) MPL histogram obtained from multiple dark-field images. Red line is a Gaussian fit, centered at 50 kDa/nm, with 11 kDa/nm full-width-at-half-maximum. Vertical dashed line indicates the MPL value expected for a single cross-β structural unit with 0.48 nm intermolecular spacing. See also Figs. S1 and S7.