Figure 2. Chemical structures of the two types of substrates, and the catalytic cofactor in photolyases.
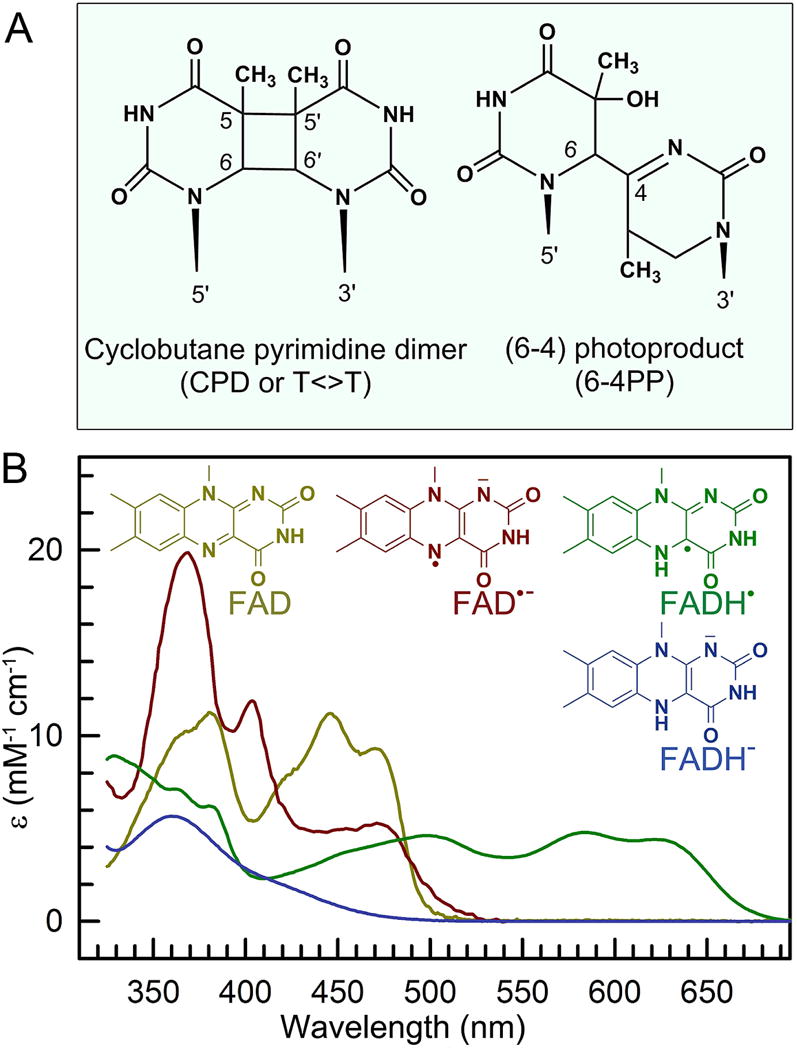
(A) Chemical structures of two UV-induced DNA photolesions, the more common cyclobutene pyrimidine dimer (CPD, ~80%), and the less common pyrimidine-pyrimidone (6-4) photoproduct (6-4PP, ~20%). (b) Absorption spectra of four redox states of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) in photolyases and their corresponding structures.
