Figure 3.
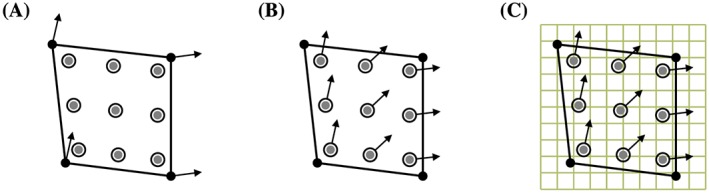
Prolonging the elastic force density from the Lagrangian mesh onto the Eulerian grid. Starting with an approximation to the force density at the nodes of the Lagrangian mesh A, we use the interpolatory FE basis functions to determine the force density at interaction points that are defined by a quadrature rule B, and then spread those forces from the interaction points to the background Eulerian grid using the smoothed delta function δ h(x) C. This approach permits Lagrangian meshes that are significantly coarser than the Eulerian grid so long as the “net” of interaction points is sufficiently dense. Denser nets of interaction points can be obtained, for instance, by increasing the order of the numerical quadrature scheme
