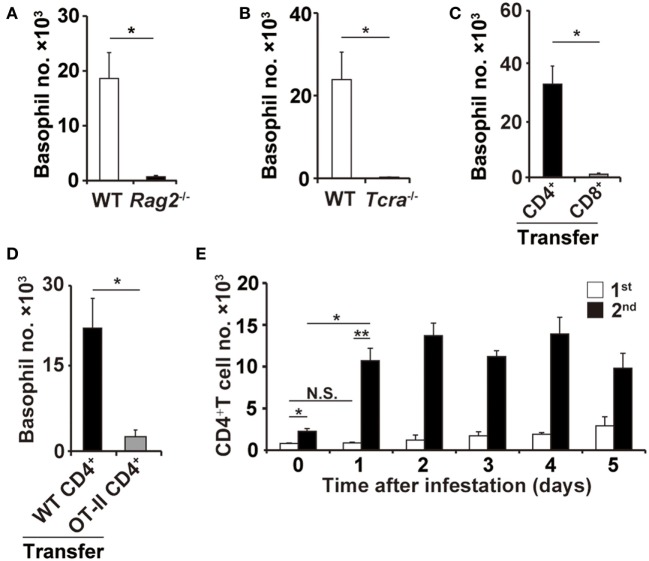
Figure 2.
CD4+ T cells are essential for basophil accumulation at the second tick-feeding site. (A,B) Wild-type (WT), Rag2−/−, or Tcra−/− mice were infested twice with ticks. The number of basophils (mean ± SEM, n = 3 each) at the second tick-feeding site in each mouse strain was examined on day 2 of infestation. (C) CD4+ or CD8+ T cells were prepared from the spleen of WT mice and adoptively transferred to Rag2−/− mice. Recipient mice were infested twice with ticks, and the basophil number at the second tick-feeding site (mean ± SEM, n = 4 each) was examined as in (A,B). (D) CD4+ T cells isolated from WT or OT-II Tg/Rag2−/− mice were adoptively transferred to Rag2−/− mice, and the basophil number (mean ± SEM, n = 4 each) at the second tick-feeding site of recipient mice was examined as in (C). (E) WT mice were infested once or twice with ticks, and the number of CD4+ T cells at the first (white bars) and second (black bars) tick-feeding sites was examined (mean ± SEM, n = 3 each). All the data shown are representative of three independent experiments. N.S., not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.