Figure 4.
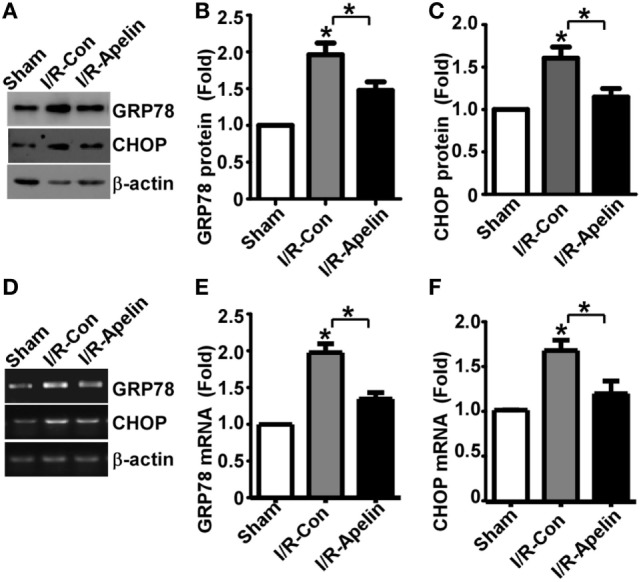
Low dose of apelin-36 inhibits cerebral I/R injury-induced GRP78 and CHOP elevation in rats. (A) Rats were subjected to vehicle or apelin-36 treatment at 2 h after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) procedure. The brain lysates of MCA territory were resolved on 8–12% Tris–Glycine sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. GRP78 and CHOP were detected by GRP78 and CHOP antibodies, respectively. β-actin served as an internal control was detected by β-actin antibody. (B) and (C) Quantification of CHOP and GRP78 protein expression, respectively. Apelin represents apelin-36. (D) Rats were subjected to vehicle or apelin-36 treatment at 2 h after MCAO procedure. The mRNA of MCA territory was extracted and RT-PCR was performed. The PCR products of GRP78 and CHOP were resolved on 1.5% agarose gel, respectively. β-actin was served as an internal control. (E,F) Quantification of CHOP and GRP78 mRNA expression, respectively. Apelin represents apelin-36. Values represent mean ± SEM. N = 5, *p < 0.05 by ANOVA followed by Tukey test.
