FIG. 5.
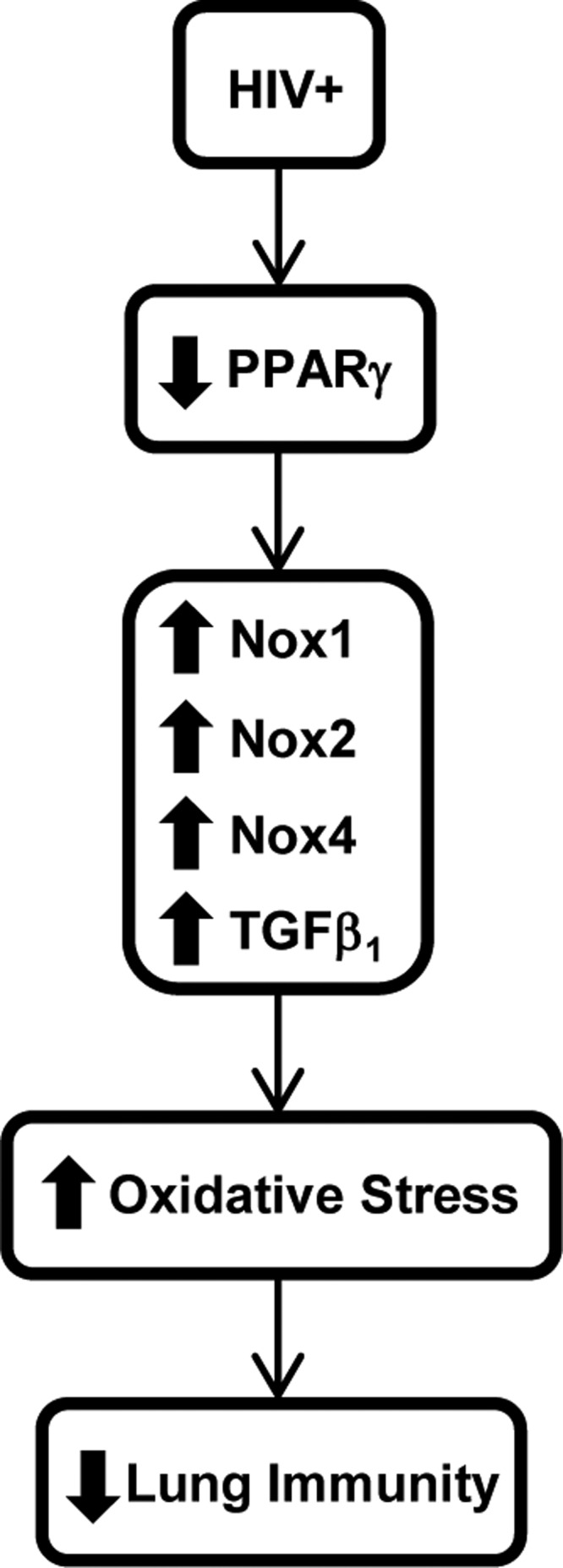
Hypothetical schema of the molecular mechanisms involved in HIV-associated lung immune dysfunction. Chronic HIV infection is associated with impaired lung immunity through decreases in AMs PPARγ expression. Attenuation of PPARγ increases AMs expression of Nox isoforms, and TGFβ1, which, in turn, enhances lung oxidative stress. This increase in lung oxidative stress causes the lung immune dysfunction observed in HIV-infected individuals.
