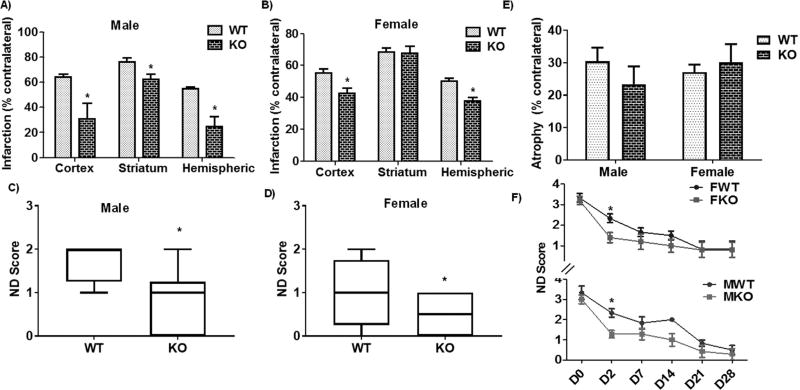
Fig. 3.
Effect of stroke on infarct volume and ND score in global P2X4R KO mice. (A) Volume was significantly reduced (p < 0.05 vs. WT littermate, two-tailed Student’s t-test, n, KO = 6 WT = 9) in cortical, striatal, and total hemispheric infarct in global KO male mice. (B) Female global KO mice displayed a similar reduction in the volume of cortical and total hemispheric infarct (p < 0.05; KO vs. WT littermates, two-tailed Student’s t-test; KO = 6,WT = 8) but not in the striatum. (C-D) ND scores confirmed acute behavioral benefits in both sexes as compared to WT controls (*p < 0.05; KO vs. WT; Mann-Whitney U test). We did not observe a change in (E) tissue atrophy or (F) ND score between global KO and WT mice for males (M) or females (F) at a chronic stage of stroke (day 30). However, a two-way ANOVA (genotype vs time) analysis in male [F (1, 66) = 16.07; p = 0.002)] as well as female [F (1, 54) = 3.927; p = 0.05] suggested a main effect of genotype (KO = 6 and WT = 8). Further, a multiple comparison analysis at individual time point between KO and WT of both sexes showed a significant difference in ND score at day 2 after stroke (*p < 0.05 vs. WT; Mann-Whitney-U test;) (FWT-male WT, FKO-Female KO; MWT-male WT, MKO-male WT).