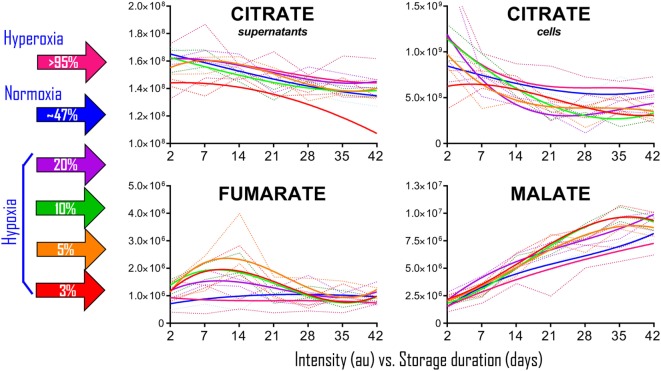
Figure 2.
Packed red blood cell (RBC) storage under controlled hemoglobin oxygen saturation conditions recapitulates high-altitude hypoxia-induced decreases in citrate and accumulation of fumarate/malate. RBCs were stored under normoxic conditions (untreated–SO2 = 47 ± 21, mean ± SD—solid blue line), hyperoxia (SO2 > 95%—solid purple line), or four hypoxic conditions (SO2 = 20, 10, 5, or <3%—solid purple, green, orange, and red lines, respectively). Supernatant citrate was significantly lower than controls (p < 0.05) in SO2 < 3% hypoxic RBCs at all tested time points. Fumarate was significantly higher than controls (p < 0.05) at storage day 7 and 14, while malate at day 14 onward in all hypoxic RBCs when compared to controls and hyperoxic counterparts. Dotted lines indicate ranges (same color-code—lighter tone). All data points on x axis were tested (n = 4).