FIGURE 1.
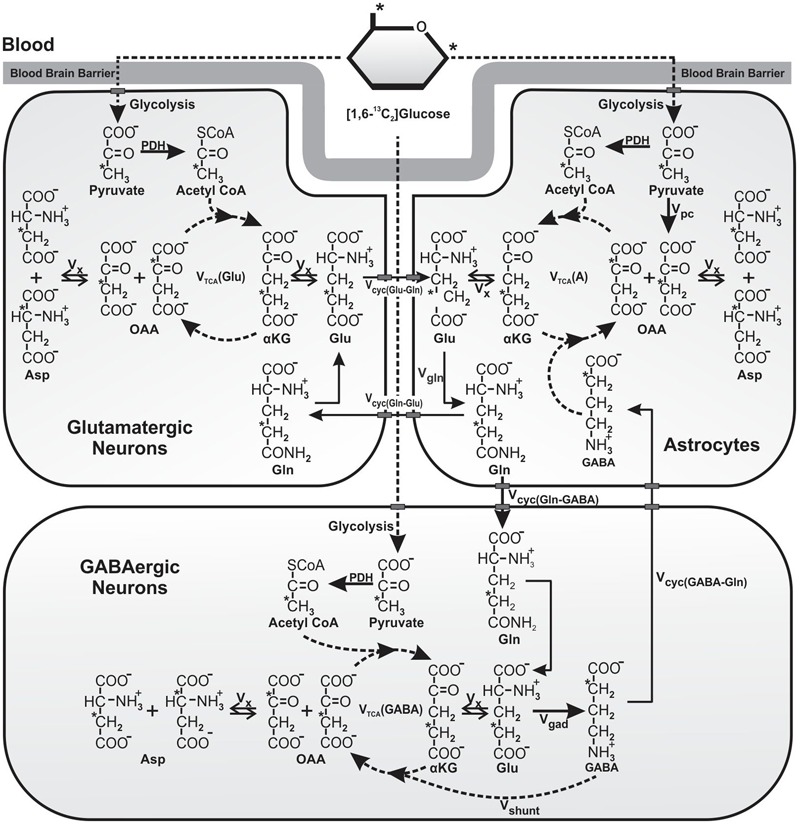
Schematic of 13C labeling of amino acids from [1,6-13C2]glucose. Metabolism of [1,6-13C2]glucose via glutamatergic and GABAergic TCA cycles labels [4-13C]glutamate, which is decarboxylated to [2-13C]GABA by GAD enzyme present specifically in GABAergic neurons. Labeling of [4-13C]glutamine occurs from [4-13C]glutamate and [2-13C]GABA via glutamate–glutamine and GABA–glutamine cycle. Further metabolism of [4-13C]glutamate and [2-13C]GABA in the corresponding TCA cycle incorporates label into [2-13C]/[3-13C]glutamate and [3-13C]/[4-13C]GABA, respectively. [3-13C]Pyruvate, the glycolytic product of [1,6-13C2]glucose is also metabolized by pyruvate carboxylase pathway (PC), and incorporates label into [2-13C]glutamine, [2-13C]glutamate, and [4-13C]GABA. For the simplicity, 13C labeling of amino acids from [1,6-13C2]glucose via the first turn of TCA cycle is depicted. Abbreviations used are: αKG, α-ketoglutarate; OAA, oxaloacetate; Asp, aspartate; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; Vcyc(GABA-Gln), GABA–glutamine cycling flux; Vcyc(Glu-Gln), glutamate–glutamine cycling flux; Vgad, glutamate decarboxylase flux; Vgln, glutamine synthesis rate; Vpc, pyruvate carboxylase flux; Vshunt, flux of GABA shunt; Vtca(A), Astroglial TCA cycle flux; Vtca(GABA), GABAergic TCA cycle flux; Vtca(Glu), glutamatergic TCA cycle flux; Vx, exchange rate between α-ketoglutarate and glutamate. ∗Represents the position of 13C carbon.
