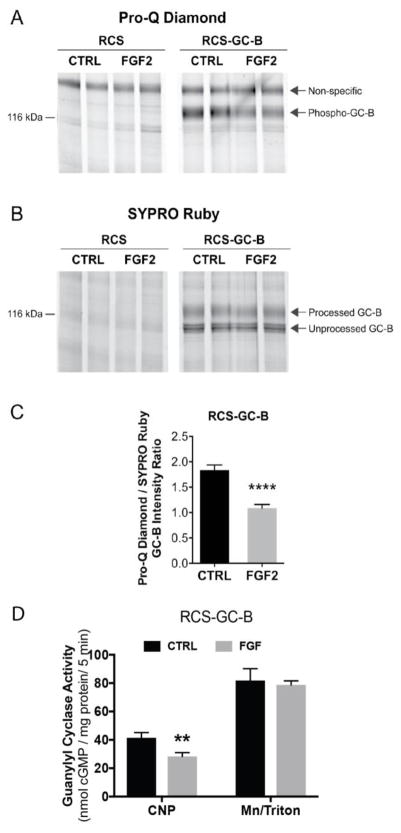
Figure 5. ProQ Diamond staining indicates that FGF exposure causes GC-B dephosphorylation.
RCS cells were transduced with an empty virus (RCS) or an adenovirus expressing wild type GC-B (RCS-GC-B). Cells were exposed to 1 μg/ml heparin with or without 100 ng/ml FGF2 for 20 min. Membranes were prepared, immunoprecipitated, and fractionated by SDS-PAGE. The gels were stained with ProQ Diamond followed by SYPRO Ruby. (A and B) Endogenous GC-B in RCS cells was below the detectability limit for ProQ and SYPRO staining (left 4 lanes), but GC-B in virally transduced cells was visible as a band at ~130 kDa (4 right lanes). (C) Densitometry measurements of the ratio of intensities of the phospho-GC-B (ProQ) and total processed GC-B (SYPRO) bands (results are from 8 determinations and 4 independent experiments). (D) GC assays of the same 8 sets of crude membranes prepared for (C) under CNP-stimulated or detergent-stimulated conditions. ** and **** indicate significance at p<0.01 and 0.0001, respectively, using an unpaired, two-tailed student’s t-test.