Fig. 1.
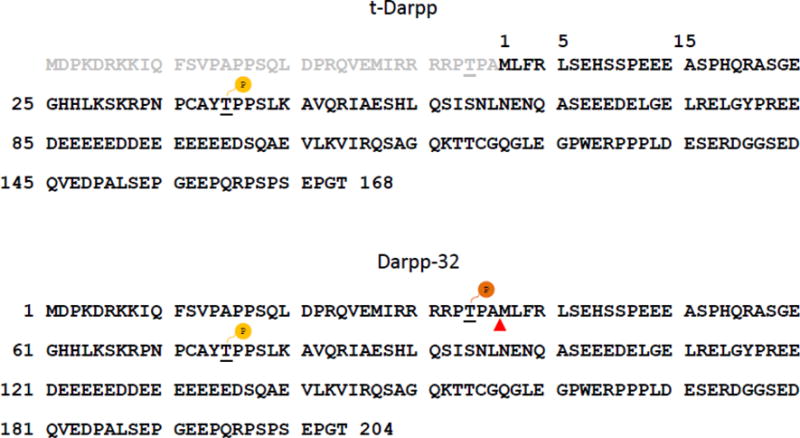
Amino acid sequences of human Darpp-32 protein (lower panel) and its truncated form t-Darpp (upper panel). Full-length Darpp-32 is a bifunctional phosphoprotein whose role is determined by its phosphorylation state. Darpp-32 phosphorylated at threonine 34 (T34) acts as an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). When it is phosphorylated at threonine 75 (T75), Darpp-32 is converted into an inhibitor of protein kinase A (PKA). t-Darpp is lacking the amino-terminal 36 amino acids of full-length Darpp-32, resulting in the absence of the T34 phosphorylation site. The T75 residue is renumbered as threonine 39 (T39) in the t-Darpp protein. Phosphorylation at T39 is crucial for t-Darpp’s effects on trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells [17].
