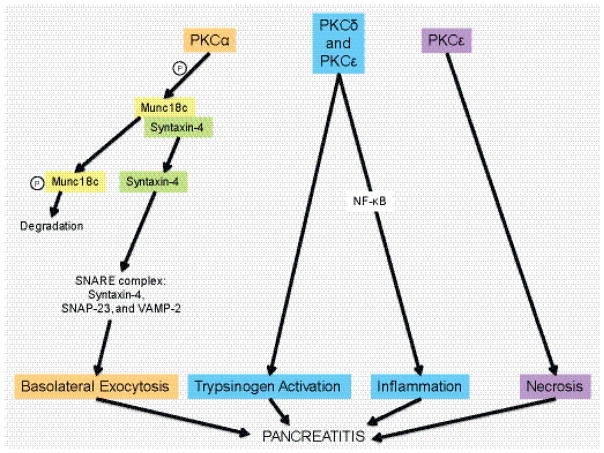
Figure 4.
Schematic of how PKD isoforms contribute to pancreatic inflammation (pancreatitis). PKCα can aid basolateral exocytosis via phosphorylation of Munc18c. This leads to Munc18c degradation and release of Syntaxin-4 and formation of the SNARE complex. PKCε has been implicated in necrosis linked to pancreatitis and both, PKCδ, and PKCε also contribute to trypsinogen activation and activation of NF-κB, which drives inflammation.