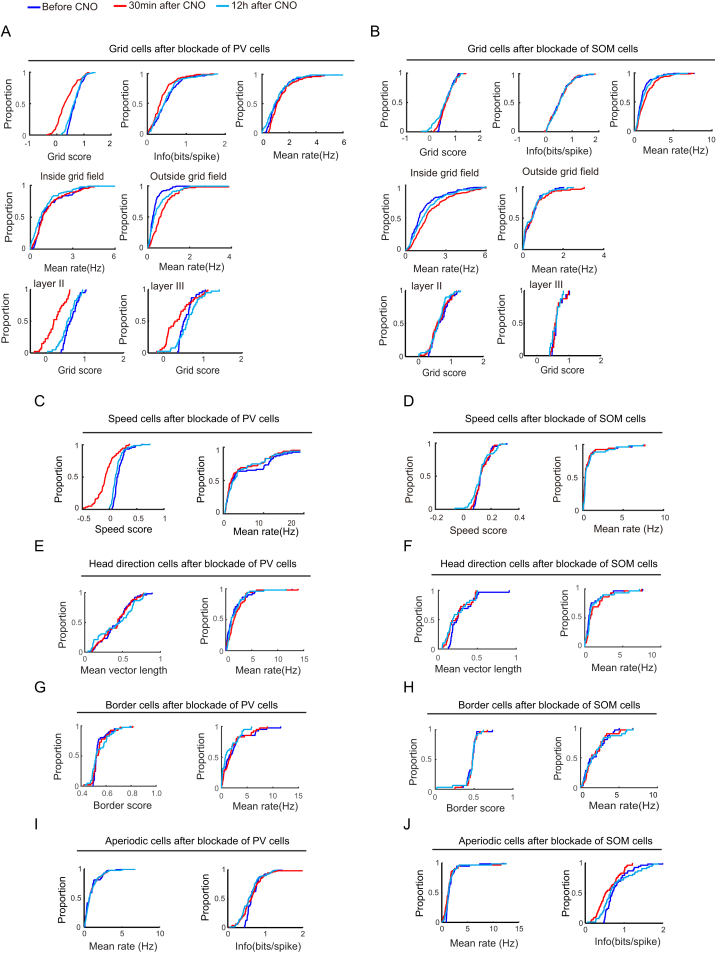
Figure S4.
Absolute Scores for Multiple Properties of Neural Firing during Baseline and 30 min and 12 hr after CNO, Related to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6
While Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 show difference scores (30 min–baseline or 12 hr–baseline), the present figure shows absolute scores for each of the three trials involved.
(A) (Upper panel) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing significant decrease in grid score and spatial information of grid cells 30 min after CNO-induced inactivation of PV interneurons but not 12 hr later. Mean firing rate of grid cells exhibits a small but significant increase after the inactivation. (Middle panel) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing increase in mean firing rate outside but not inside grid fields after inactivation of PV interneurons. (Bottom panel) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing stronger decrease of grid scores in layer-II than layer-III grid cells 30 min after CNO.
(B) (Upper panel) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing no change in grid score, or spatial information of grid cells after CNO-induced inactivation of SOM interneurons. The mean firing rate of the grid cells is increased after CNO. (Middle panel) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing significant increase in mean firing rate inside but not outside grid fields after inactivation of SOM interneurons. (Bottom panel) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing no change of grid scores in layer II or layer III 30 min after inactivation of SOM interneurons.
(C and D) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing significant decrease in speed-rate correlation (speed score) of speed cells after inactivation of PV interneurons (C, left panel), but not after inactivation of SOM interneurons (D, left panel). The mean firing rate of the speed cells showed a small but significant decrease after inactivation of PV interneurons (C, right panel) or SOM interneurons (D, right panel).
(E and F) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing no change in mean vector length of head direction tuning after inactivation of PV (E, left panel) or SOM interneurons (F, left panel). The mean firing rate of the head direction cells showed a slight but significant increase after CNO inactivation of PV interneurons (E, right panel) but no significant change in mean firing rate of head direction cells after CNO-induced inactivation in the SOM group (F, right panel).
(G and H) Cumulative frequency diagrams indicating no change in border scores or mean firing rates of border cells after CNO in the PV group (G) and the SOM group (H).
(I and J) Cumulative frequency diagrams showing that mean firing rate (I, left panel) and spatial information (I, right panel) did not change in aperiodic spatial cells after inactivation of PV interneurons, whereas inactivation of SOM interneurons reduced spatial information in these cells (J, right panel). Mean firing rate was not changed (J, left panel).