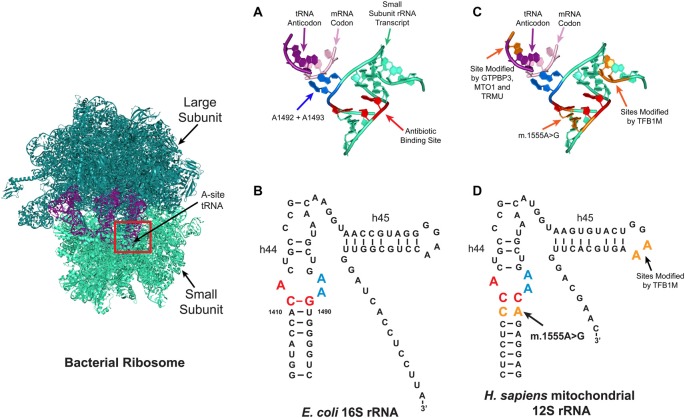
Figure 3.
Aminoglycoside ribosome binding. Aminoglycosides can bind to several sites on ribosomes, with the primary prokaryotic binding site reported to be a conserved pocket in the A-site (red box) formed by helix h44 of the 16S rRNA in the small ribosomal subunit. At this site, the correct tRNA anti-codon is matched with the correct mRNA codon. (A,B) Tertiary (A) and secondary (B) structures of the bacterial A-site. In bacteria, aminoglycosides bind to three conserved nucleotides A1408, C1409 and G1491 (red). (C,D) Schematic depicting the tertiary (C) and secondary (D) structures of the mitochondrial A-site. In the human mitochondrial ribosome, patients with the m.1555A>G mutation have a new base pair formed which makes it resemble the bacterial ribosome. Four nuclear genes are reported to modify the penetrance of aminoglycoside related hearing loss (TRMU, MTO1, GTPBP3 and TFB1M), the tRNA and rRNA nucleotides modified by these enzymes are shown in orange.