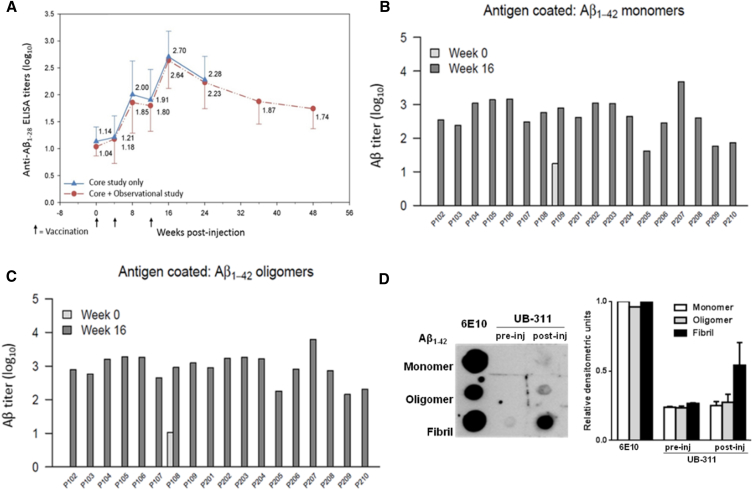
Fig. 2.
Serum anti-Aβ antibody titers assayed by ELISA and preferable targeted Aβ species visualized by dot plot after UB-311 immunization in AD patients. (A) Mean antibody response during the 24-week interventional study (solid line) in 19 AD patients treated with UB-311; 14 of 19 patients (dashed line) were followed up in an additional 24-week observational study, whose mean ADAS-Cog score was 4.9 (improvement). The mean baseline titer (pretreatment) was 1.0 log10; and 4 weeks after last vaccine boost at week 16, the titer peaked at 2.7 log10 (range: 1.8–3.7 log10). At week 48, all patients had decreasing but still positive antibody titers, measured by Aβ1–28 ELISA test. At week 16, serum samples recognized Aβ1–42 monomers (B) and oligomers (C); preimmune serum samples collected at week 0 had anti-Aβ1–42 antibody levels below quantification limit (not shown on log scale), except subjects P109 (monomer) and P108 (oligomer). (D) At week 16, analysis of serum dot plot (left panel), flanked by the positive control 6E10 mAb, reveals that the vaccine-induced anti-Aβ antibodies bind preferentially to Aβ fibrils, followed by oligomers, and the least to monomers; the densitometric measures (right panel) for the three Aβ species are the mean scales from three representative AD subjects, P105, P108, and P206. Abbreviations: AD, Alzheimer's disease; ADAS-Cog, Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale–Cognitive Subscale; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.