FIG 2.
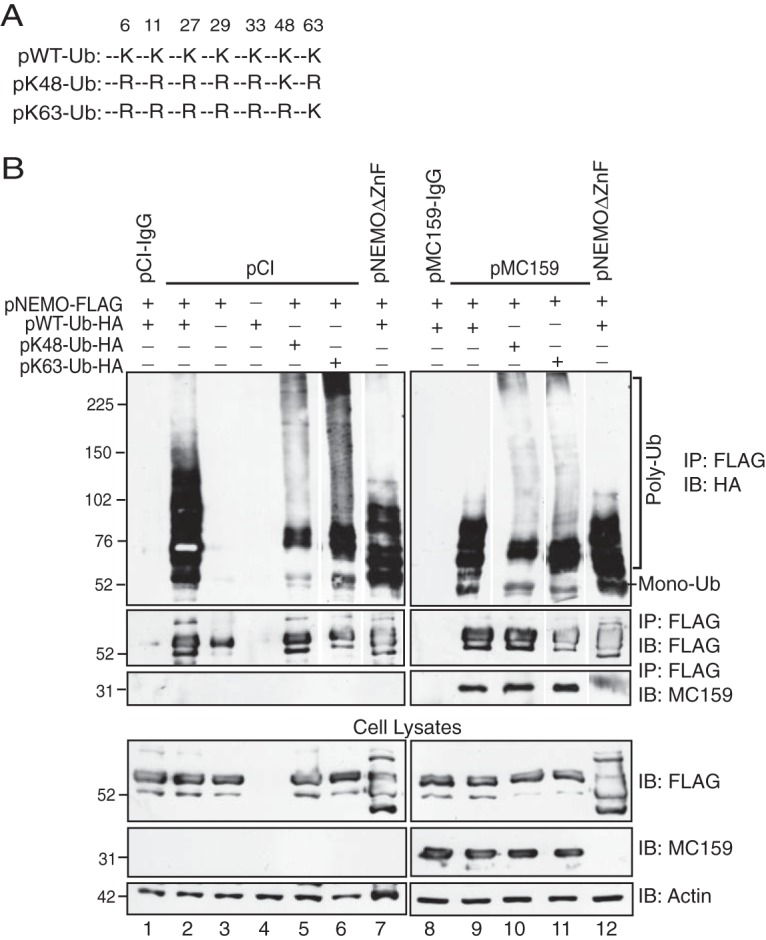
MC159 inhibits K63-linked NEMO polyubiquitination. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type or mutant Ub proteins that indicate lysine (K) or arginine (R) at a specific residue. (B) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with 250 ng pNEMO-FLAG; 250 ng of pWT-Ub-HA, pK48-Ub-HA, or pK63-Ub-HA; and 1,000 ng of either pCI, pMC159, or pNEMOΔZnF for 24 h. Next, cells were incubated in medium containing 10 ng/ml TNF for 15 min. Cells were lysed in Ub lysis buffer. A portion of each lysate was set aside to monitor protein expression. For the remaining clarified cellular lysates, IPs were performed by using either anti-FLAG or IgG antibodies conjugated to protein G-Sepharose beads. Immunoprecipitated samples or cellular lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, and proteins were transferred onto PVDF membranes for IB. Membranes were probed with the indicated antibodies to detect ubiquitinated forms of NEMO, MC159, or actin. For immunoprecipitated samples probed with anti-HA to detect ubiquitin, anti-FLAG, or anti-MC159 antibodies, lanes from the same gel were spliced to show the relevant samples for the experiment. The corresponding cellular lysates were probed by immunoblotting in a subsequent assay, avoiding the need for splicing. Monoubiquitinated (Mono-Ub) and polyubiquitinated (Poly-Ub) forms of NEMO are indicated.
